Grand Central Station NY WWII

Don’t hold your breath for breaking up banks. Gas tax is more interesting: keep oil prices low and off you go. Could be a huge source of revenue, and Trump needs a few of those.
• Trump Weighs Breaking Up Wall Street Banks, Raising Gas Tax (BBG)
President Donald Trump said he’s actively considering a breakup of giant Wall Street banks, giving a push to efforts to revive a Depression-era law separating consumer and investment banking. “I’m looking at that right now,” Trump said of breaking up banks in a 30-minute Oval Office interview with Bloomberg News. “There’s some people that want to go back to the old system, right? So we’re going to look at that.” Trump also said he’s open to increasing the U.S. gas tax to fund infrastructure development, in a further sign that policies unpopular with the Republican establishment are under consideration in the White House. He described higher gas taxes as acceptable to truckers – “I have one friend who’s a big trucker,” he said – as long as the proceeds are dedicated to improving U.S. highways.
During the presidential campaign, Trump called for a “21st century” version of the 1933 Glass-Steagall law that required the separation of consumer and investment banking. The 2016 Republican Party platform also backed restoring the legal barrier, which was repealed in 1999 under a financial deregulation signed by then-President Bill Clinton. A handful of lawmakers blame the repeal for contributing to the 2008 financial crisis, an argument that Wall Street flatly rejects. Trump couldn’t unilaterally restore the law; Congress would have to pass a new version. Trump officials, including Treasury Secretary Steven Mnuchin and National Economic Council Director Gary Cohn, have offered support for bringing back some version of Glass-Steagall, though they’ve offered scant details on an updated approach. Both Mnuchin and Cohn are former bankers who worked for Goldman Sachs.

A deeply unstable economy.
• Life After Oil Makes Real Estate Canada’s New Economic Crutch (BBG)
Two things happened last week that were a reminder of just how vital real estate has become to Canada’s economy. On Friday, Statistics Canada released GDP data that showed February was a banner month for sectors linked to housing. The real estate industry, residential construction, financial and legal services generated a combined 0.5% increase in output, the biggest one-month gain since 2014. Without those, the overall economy would have contracted slightly in February. A day earlier, the Ontario government released a budget that projects land transfer taxes will surpass C$3 billion ($2 billion) in the current fiscal year, from C$1.8 billion three years ago. For the province, it’s the difference between a balanced budget and a deficit.
Measures of housing’s contribution to the economy are imprecise, but estimates largely put the direct contribution in excess of 20%. It’s much more than that once you add all the indirect effects, with benefits spread widely from lawyer fees to government revenue and increased retail purchases through so-called wealth effects as rising home equity values prompt households to ramp up consumption. The big worry is that Canada has moved from a reliance on oil to a reliance on real estate. The influence of housing on the economy is so pervasive that it won’t take much of a slowdown to act as a major drag on the economy, said Mark Chandler, head of fixed-income research at RBC Capital Markets in Toronto.
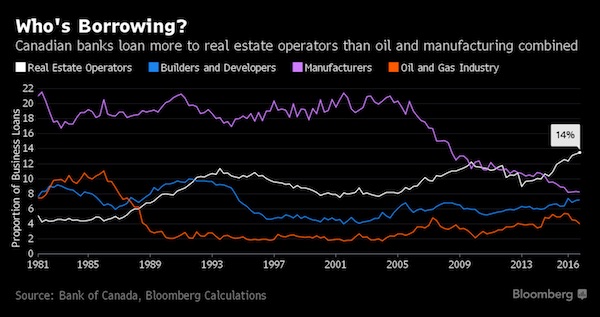
“You don’t need a collapse in house prices, you don’t need housing starts to be cut in half for weaker real estate sector to have a significant effect on GDP and incomes,” Chandler said. RBC’s ballpark estimate is that a 10% decline in national home prices would knock a full percentage point off growth. A Toronto Dominion Bank report from 2015 found the housing wealth effect has been responsible for about one-fifth of all growth in consumption since 2001. “A lot of the strength we have seen in consumption is housing related,” said Brian DePratto, the economist who wrote the 2015 report. If you strip out the direct and indirect impact from housing on the economy, “you are talking about a much lower trend pace of growth.”

Subprime.
• How Did Home Capital Get Into Trouble? (BBG)
The world is suddenly paying attention to Home Capital, the tiny Canadian mortgage lender that’s on the ropes. The stock is plunging, it faces a run on deposits and regulators are probing management’s disclosure of fraudulent mortgages. Its troubles are raising questions: Is this an isolated case of a struggling mortgage company, or early signs of cracks forming in Canada’s red-hot housing market?
1. How did Home Capital get into trouble? It started in 2014 when the company, formed 31 years ago by Gerald Soloway, failed to screen a pile of questionable mortgages brought in by outside brokers. Some 45 brokers falsified income information on borrowers, prompting Home Capital to cut ties with them, leading to a drop in new business. This eventually led to an investigation by the Ontario Securities Commission, which said on April 19 that Home Capital had misled investors by not disclosing the fraud until five months after they became aware of the problem.
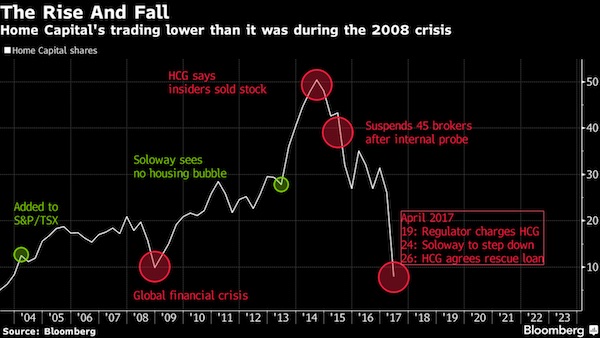
2. Will Home Capital fail? There are plenty of signs of stress. The stock has plunged almost 75% this year, cutting its market value to about C$515 million, from C$3.5 billion in 2014. Most pressing is the run on deposits. Customers pulled C$1.5 billion from high-interest savings accounts in four weeks, cutting the balances to C$500 million. The company has another C$13 billion in GICS. As these 30- and 60-day deposits come due, more withdrawals may follow. Without a deposit base, Home Capital can’t fund new mortgages. Home Capital hired investment bankers for a possible sale, though there is likely as much interest in the loan book as the company itself. Commercial banks may be interested, precluding any need for a government bailout. Financial regulators say they are watching closely.
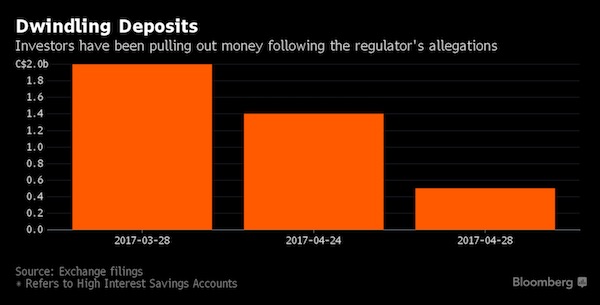
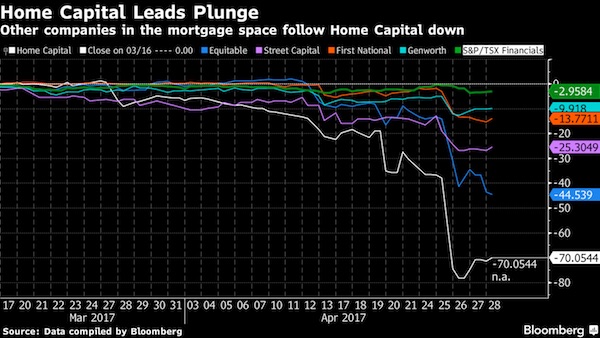
3. Will this fallout spread to other lenders? Possibly. Home Capital competes with other companies in the so-called alternative mortgage space. They cater to small-business owners, new immigrants and other people who can’t get mortgages from the big commercial banks. It’s a niche segment but growing, accounting for almost 13% of the market. Unlike in the U.S. housing crash when loan defaults soared, there is little evidence of faulty loans so far. Home Capital’s delinquency rate, for example, was just 0.20% as of February. Still, shares of rivals First National and Equitable have been dragged lower by the Home Capital woes as investors fear contagion.

Beijing sends a lot of signals, but it cannot make good on them without risking the economy, and everybody knows it. It’s all based on the idea that a centralized economy can be forced into a smooth descent, but that’s just a fallacy.
• China Leverage Rising At ‘Alarming Pace’: Central Bank Official (R.)
China’s level of leverage is rising at an “alarming pace”, particularly in the finance sector, a senior central bank official said in a commentary, amid growing concern by the country’s senior leaders over financial security. The official Xinhua news agency on Monday cited Xu Zhong, head of the People’s Bank of China’s research bureau, as saying the country needed to deleverage at a “proper pace” to reduce financial sector debt and avoid systemic financial risk. “China’s overall leverage level is reasonable but is rising at an alarming pace, especially in the financial sector,” Xu said. The original commentary was published in business journal Caijing Magazine. Xu said high levels of stimulus spending from government paired with poor corporate management and financial supervision were key factors causing rising levels of leverage, Xinhua said.
He added the government should stick to “prudent and neutral” monetary policy, reduce emphasis on economic growth targets, and improve corporate governance so authorities did not have to step in so frequently to help companies out. “Financial security is achieved via reforms, not bail-outs,” Xinhua reported Xu as saying. Last week President Xi Jinping called for increased efforts to ward off systemic risks and help maintain financial security. Analysts say financial risk and asset bubbles pose a threat to the world’s second-largest economy if not handed well. Former Chinese finance minister Lou Jiwei also said last month that high leverage was the biggest risk facing China’s economy because debt has piled up despite government efforts to deleverage. The Bank for International Settlements warned last year that excessive credit growth in China is signaling an increasing risk of a banking crisis in the next three years.

Well, maybe they’ll get serious because it’s about Treasuries this time, and foreign banks. Then again, these are primary dealers in Treasuries.
• UBS, BNP, RBS Get Subpoenas in US Treasuries Probe (BBG)
Federal prosecutors have subpoenaed several banks as part of a criminal investigation into possible manipulation of the U.S. Treasuries market, according to people familiar with the matter. The Justice Department issued subpoenas last month to banks including UBS, BNP Paribas and the Royal Bank of Scotland seeking information on the $14 trillion market, said two people, who asked not to be named because the investigation is confidential. U.S. authorities have been examining the U.S. Treasuries market for roughly two years. In November 2015, Goldman Sachs disclosed that U.S. authorities had sought information related to its trading of when-issued securities, which are among the least transparent instruments in the world’s largest debt market. When-issued securities act as placeholders for bills, notes or bonds before they’re auctioned. The instruments change hands over the counter, with lifespans of just days. There’s scant public information on trading volumes or the market’s biggest players.
[..] The Justice Department in late 2015 asked about when-issued securities as part of broader requests for documents it sent to most or all of the roughly two dozen primary dealers in U.S. Treasuries, a person familiar with the matter told Bloomberg News at the time. UBS, BNP Paribas and RBS are primary dealers in U.S. Treasuries. Authorities haven’t accused any of the banks of wrongdoing. Trading of these instruments is also the subject of several lawsuits against primary dealers filed since July 2015. In them investors allege that traders at global banks colluded to artificially inflate the price of the when-issued securities, which allow the banks to sell U.S. debt before they own it. Then they bought the debt at auctions for an artificially suppressed price, unfairly profiting at investors’ expense, the lawsuits contend. The banks are scheduled to file motions to dismiss those lawsuits once the lead counsel for the plaintiffs is chosen.

Increased health care spending presumably adds to GDP, so why worry?
• The US Health Care Industry Is Bound To Collapse Soon (NYP)
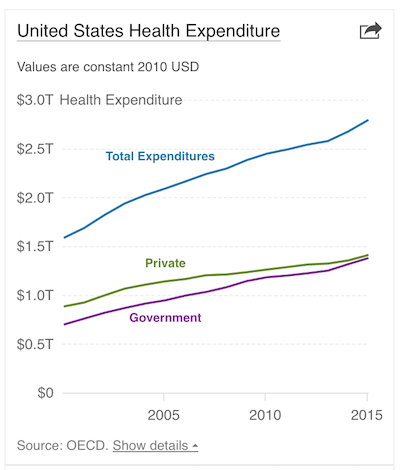
As industry spending and debt servicing rage out of control, health care is ranked as the No. 1 US “systemic recession risk” in a new report. The sums at stake are staggering: Spending in the sector accounted for $3.3 trillion in 2015, and is 18% of the US economy today. The industry generates 16% of private sector jobs nationwide, up from 10% in 1990. US health care spending is forecast to grow by an average 5.6% annually in the coming decade, according to a report by the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), a projection based on no changes out of Washington and in the Affordable Care Care through 2025. Meanwhile, national spending on health care is forecast to outpace US GDP growth by 1.2%. CMS has estimated that spending will comprise 19.9% of GDP by 2025, up from 17.8% in 2015.
“There’s no question that rising health care costs are hurting our overall economy,” said New York-based financial adviser Michael Mondiello. “With consumer spending accounting for some 70% of economic activity, the more we spend on health care, the less we have to purchase other things like a vacation or to save for retirement.” [..] The first murmurs of early trouble may have been detected. “Companies in the health care sector are starting to lay people off,” said John Burns, CEO of John Burns Real Estate Consulting.. [..] “Health care companies borrowed too much money, and have grown their debt faster than their revenue, so you have to have a pullback.”
[..] In a report published by Burns, health care is identified as the largest systemic risk to the economy, of the three sectors Burns examined, which also included technology and automotive. The conventional wisdom points to US demographic trends, and an aging population, as supportive of the long-term strength, but the report shows industry growth has surpassed what is sustainable:
• Health care company debt is up 308% since 2009.
• The number of hospitals in health systems has expanded by 26% since 1999.
• The yearly medical costs for a family of four have jumped 189% since 2002, from $9,000 to $26,000.
“It could be like a Lehman Brothers scenario, where a couple of big health care companies take the economy down,” Burns told The Post.

As usual, a long essay from John. A few bites:
• Exhaustion Gaps and the Fear of Missing Out (John Hussman)
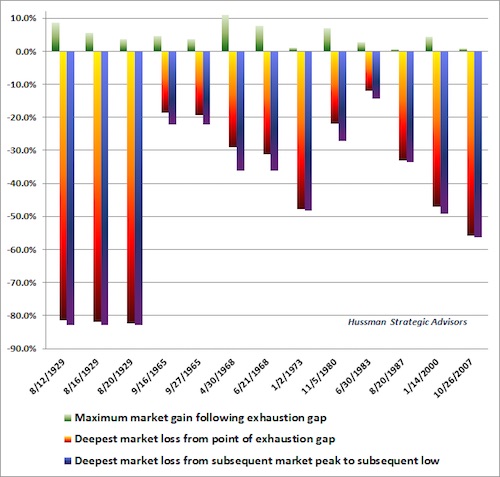
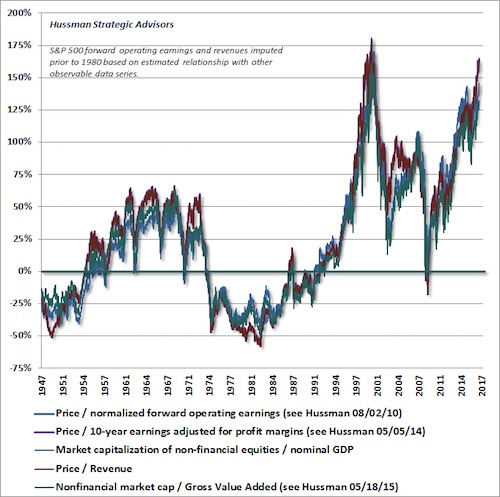
To offer a sense of the market return/risk profile that has typically been associated with exhaustion gaps at overvalued, overbought, overbullish extremes, the chart below shows the maximum gain and maximum loss in the market as measured from each instance to the subsequent bear market low. Multiple exhaustion gaps in the same market cycle are depicted separately. I recognize that my regular comments about the likelihood of the S&P 500 losing half or more of its value over the completion of this cycle may seem preposterous. A review of market history may help to understand these expectations, which are consistent with both the valuation evidence later in this comment, and with the outcomes that have typically completed prior speculative market cycles.
Two caveats are important here. First, given the simplicity of the conditions that define an exhaustion gap above, and their reliance on daily market behavior, it’s not clear that investors should wait for such gaps in future market cycles if other danger signs are already present. The best way to view these exhaustion gaps, I think, is that they represent points, late in a bull market cycle, where investors become overwhelmed by fear of missing out (FOMO), leaving a lopsided equilibrium where the remaining pool of potential buyers evaporates and the pool of potential sellers becomes saturated. Conversely, it seems likely that simple daily signals like the exhaustion gaps above could be misleading in the future, if more robust measures still indicate persistent risk-seeking among investors.
As a reminder of where market valuations stand, based on what actually works across market cycles, the chart below presents several of the most historically reliable equity valuation measures we track. We can form expectations about the likely range of market losses over the completion of this cycle by asking what amount of retreat would be required to bring these measures to either: a) the highest level of valuation reached at any previous bear market low, or b) the historical norm of each measure. Emphatically, these estimates do not assume that valuations will move below their historical norms at the next bear market low (as they did, in fact, as recently as the 2009 low). The smallest expected loss estimate comes in at -45.6%, while the largest loss estimate (taking each measure to its respective historical norm) is -62.1%. The average range of estimated market losses is -47.7% to -60.1%, while the median range is -45.6% to -62.0%.

I think I already know which way Trump will lean.
• Barack Obama Cashes In, But Harry Truman And Jimmy Carter Refused (IC)
It used to be the norm for presidents to retire to ordinary life after their stint in the White House — just ask Harry Truman. When the Democratic president was getting ready to leave the White House in 1953, he was approached by many employers. The Los Angeles Times noted that if he was “unemployed after he leaves the White House it won’t be for lack of job offers … but [he] has accepted none of them.” One of those job offers was from a Florida real estate developer, asking him to become a “chairman, officer, or stockholder, at a figure of not less than $100,000” — the sort of position that is commonplace today for ex-politicians. Presumably, had Truman taken the position, it would have been a good deal for both parties: the president’s prestige and connections would also enrich the company.
Truman declined. “I could never lend myself to any transaction, however respectable, that would commercialize on the prestige and dignity of the office of the presidency,” he wrote of his refusal to influence-peddle. Although he had access to a small pension from his military service, Truman had little financial support after leaving office. He moved back into his family home in Independence, Mo., and insisted on being treated like anyone else. He would tell people not to call him “Mr. President,” and settled on a fairly ordinary routine once he was back in Independence. He would take a morning walk through the town square. He kept an office nearby where he would answer mail from Americans. He chose to engage with just about anyone who walked into his office — not only people who wrote him big checks, or invited him onto their private yachts and private islands.
“Many people,” he once said, “feel that a president or an ex-president is partly theirs — they are right to some extent — and that they have a right to call upon him.” Indeed, his office number was even listed in a nearby telephone directory. He eventually agreed to write a memoir for Life magazine, but it was a lengthy project that provided far from luxurious stipends. Truman’s modest life post-presidency moved Congress in 1958 to establish a pension system that provides an annual cash payout as well as expenses for an office and staff. Gerald Ford nevertheless shattered precedent when he joined the boards of corporations such as 20th Century Fox, hit the paid speech circuit, and was made an honorary director by Citigroup.
But his successor, Jimmy Carter, who grew up in a modest home in Plains, Georgia, did not follow Ford’s example. He refused to become a professional paid speaker or join corporate boards. He moved back to Plains, and was welcomed home by a crowd of neighbors and supporters. He quickly made himself busy as a nonprofit founder and a volunteer diplomat. He did make money post-presidency — but by serving ordinary people, not elites. He wrote dozens of best-selling books bought by millions of people across the world — the post-presidency equivalent of small donors. Carter explained his thinking to the Guardian in 2011, telling them that his “favorite president, and the one I admired most, was Harry Truman. When Truman left office he took the same position. He didn’t serve on corporate boards. He didn’t make speeches around the world for a lot of money.”

“Rest easy America… oh, and buy every dip.”
• The Sound of One Wing Flapping (Jim Kunstler)
And suddenly the storms of early Trumptopia subside, or seem to. The surface of things turns eerily placid as the sweets of May sweep away the toils of an elongated mud season. Somebody stuffed Kim Jong Un back in his bunker with a carton of Kools and the Vin Diesel video library. France appears resigned to Hollandaise Lite in the refreshing form of boy wonder Macron. It’s been weeks since The New York Times complained about the Russians stealing Hillary’s turn as leader of the free world. We’re given to understand that Congress managed overnight to cook up a spending bill that will avert a Government shut-down until September. Rest easy America… oh, and buy every dip.
A calm surface is exactly what Black Swans like to land on, though by definition we will not know they’re out there until our reveries are broken by the sound of wings flapping. Some kind of dirty bird showed up on Canada’s thawing pond last week when that country’s biggest home loan lender suffered a 60 percent pukage of shareholder equity and had to be bailed out — not by the Canadian government directly, but by the Ontario Province’s Health Care Workers Pension Fund, a neat bit of hocus pocus that amounts to a one-year emergency loan at ten percent interest. If that’s a way for insolvent public employee pension plans to find enough “yield” to meet their obligations, then maybe that could be the magic bullet for the USA’s foundering pension funds.
The next time Citibank, Goldman Sachs, JP Morgan, and friends get a case of the Vapors, let them be bailed out by the Detroit School Bus Drivers’ Pension Fund at ten percent interest. That ought to work. And let Calpers take care of Wells Fargo. The situation across Western Civilization is as follows: virtually every major financial institution has become a check-kiting operation or a Ponzi scheme, and we’ve reached the point where they can only pretend to be rescued. Bailout or not, the Toronto-based Home Capital Group is still stuck with shit-loads of non-performing sub-prime mortgage loans — its specialty — and Canada’s spectacular real estate bubble has hardly begun to pop. The collateral is starting to turn, like dead meat in the May sunshine, and the odium will waft across the border.

“It is truly astonishing that the man who inspired (as personal secretary) and implemented (as finance minister) the policies of President François Hollande could be branded as something radically new.”
• Emmanuel Macron Has Taken French Voters For Granted. Now He Risks Defeat (G.)
The rise of Macron is characteristic of the age of spin doctors: it illustrates both their power and their limits. It is truly astonishing that the man who inspired (as personal secretary) and implemented (as finance minister) the policies of President François Hollande could be branded as something radically new. To achieve this feat, spin doctors resorted to celebrity-building in ways previously unknown in French political life. Macron was new because he was young and handsome, and because he had never been elected before. He appeared repeatedly on the front pages of Paris Match with his wife, whose name is chanted by his supporters at his rallies. In the final weeks of the campaign Macron was so careful not to expose the true nature of his programme (which amounts to little more than the unpopular liberalism-cum-austerity implemented by Hollande) that his speeches degenerated into vacuous exercises in cliche and tautology.
The strategy worked up to a point: he qualified for the second round. Yet its limits are also clear. Last spring, France saw nationwide protests against the labour laws that Macron had largely designed. The opposition was not only to their content, but also to the manner in which they were passed: the government bypassed a parliamentary vote. During these demonstrations police used high levels of violence, yet Macron never uttered a word to calm things down. He has already announced that he would resort to governing by decree if needed, and it is easy to anticipate increased social tensions by the autumn. To those who would oppose him, Macron would answer that he is implementing the programme on which he was elected. Theoretically, Macron should defeat Le Pen hands down. The problem is that the meaning of such a result would be unclear: how many would have voted for him, and how many against her?

The EU can do what it wants with the UK, because whatever it is, the Brits will blame each other for anything that goes wrong. No need for divide and conquer, there’s a hopeless divide already; Brussels can focus on conquer.
• How Juncker’s Downing Street Dinner Turned Sour (G.)
The meeting last Wednesday started with a kiss on the cheek, gratefully immortalised by the photographers on Downing Street’s pavement. It ended with a withering putdown: “I’m leaving Downing Street 10 times more sceptical than I was before,” Juncker told his host. It is said that the talks started pleasantly enough. During half of an hour of chit-chat in an anteroom, before taking their place at the dinner table, May told Juncker that she didn’t want just to talk Brexit during the evening but there were other matters of world affairs to discuss. “Like what?”, Juncker asked. In fact, little else seemed to be on the prime minister’s mind. Juncker did have a topic to raise though, and the issue at hand may just explain some of the current iciness between the two leaders.
That very morning the EU should have been shuffling around its money to deal with issues such as the migration crisis, which could not have been expected a few years ago when the bloc’s budget had been set. But on Monday morning Juncker had been made aware of an email from the UK’s permanent representative in Brussels explaining that because a general election had been announced, the British government couldn’t give its support to any changes in how the EU was going to spend its cash. Juncker smelled mischief – maybe it was a way to show the EU what trouble Britain could cause if it didn’t get its way? “What on earth is all this supposed to mean?” he is said to have asked May. Perhaps you won’t be able to talk about Brexit then, he queried, when May explained the rules of purdah, under which governments in an election are to avoid binding the hands of the next administration.
[..] it was the substance of the talks that were to cause Juncker the most unease. And it was Juncker’s despair that got to his colleagues. This was the man who through the trickiest of negotiations had always seen a path through. But when presented with May’s insistence that EU citizens in the UK would be treated in the future like any other foreign national, that trade talks needed to start before the issue of Britain’s divorce bill was settled or her claim that technically the UK owed nothing at all to the union, his lack of optimism for the future became clear. “Theresa May started by stating that the UK wanted to discuss first future arrangements, then article 50 stuff,” one source with knowledge of the dinner said.
“It felt to the EU side like she does not live on planet Mars but rather in a galaxy very far away.” She was “deluded” and appeared to be “living in a parallel universe”, Juncker told the German chancellor, Angela Merkel, in a phone call said to have taken place just moments after the delegation left Downing Street.

Absolute insanity: “..pensions are to be cut by 9% on average..”
• Greece Reaches Deal With Creditors To Pave Way For Bailout Talks (G.)
Greece has reached a preliminary deal with its creditors that should pave the way for long-awaited debt relief talks, the Greek finance minister said on Tuesday. “The negotiations are concluded,” Euclid Tsakalotos told reporters, according to state agency ANA. After overnight talks, Tsakalotos said a “preliminary technical agreement” had been achieved ahead of a 22 May meeting of eurozone finance ministers, which is required to approve the deal. Tsakalotos added he was “certain” that the agreement would enable Greece to secure debt relief measures from its creditors, which he has said is vital to spearhead recovery in the country’s struggling economy. A compromise is required to unblock a tranche of loans Greece needs for debt repayments of €7bn ($7.6bn) in July.
Under pressure from its creditors – the EU, ECB and the IMF – the government agreed earlier this month to adopt another €3.6bn in cuts in 2019 and 2020. Athens conceded fresh pension and tax break cuts in return for permission to spend an equivalent sum on poverty relief measures. A government source on Tuesday said pensions are to be cut by 9% on average, ANA said. The measures are to be approved by parliament by mid-May. However, prime minister Alexis Tsipras has said he will not apply these cuts without a clear pledge later this month on debt-easing measures for Greece. Athens also hopes to be finally allowed access to the ECB’s QE asset purchase programme, to help its return to bond markets.

So many numbers it’s easy to forget this is about people.
• Greece: Any Better Times Or More Pitfalls Ahead? (LSE)
In 2015, Greece, an EU state member since 1981 with a population of 10,846,979 people, recorded the highest level of GGD (General Government Gross Debt to GDP ratio) in the EU-28, at 176.9%. Concerning the volume index of GDP per capita in PPS (Purchasing Parity Standards) we find Greece’s GDP per capita dropped from 4% lower than the EU-28 average in 2004 to 29% lower in 2015. However, GDP is a measure of a country’s economic activity, and therefore it should not be considered a measure of a country’s well-being. If we take the AIC (Actual Individual Consumption) per capita in PPS (Purchasing Power Standard) as a better indicator to describe the material welfare of households, Greece showed an AIC index per capitalower by some 19% than the EU-28 average in 2015. Labour productivity per hour worked expressed in US $ (which means GDP per hour worked expressed in US $) was estimated among the lowest in the EU-28, at $32 in 2015.
Curiously, Greece has the highest average hours worked per year in the EU-28, at 2,042 hours, its average hourly labour cost is among the lowest in the EU-28, at €14.5, its average annual wages at US $25,211 and unemployment rate of 24.90%. 43% of pensioners live on €660/month on average, and many Greek pensioners are also supporting unemployed children and grandchildren. [..] Unemployment is a tragedy for Greece. The highest jobless rate was recorded in 2014, at 27.8%. The current level of unemployment, the highest in the EU, is about 24%. Unemployed workers between 45 and 64 years of age (currently almost one in three unemployed, around 347,400 people, whereof 280,000 are long-term unemployed, in 2009 they were one in five, or 99,000 people)- , and young unemployed people aged 15-24 (close to 50% of the total) are the most adversely affected demographics.
According to ELSTAT (Hellenic Statistical Authority) – GSEE (General Confederation of Greek Workers), nine out of ten Greeks without job do not receive unemployment benefits and 71.8-73.8% (around 807,000 people) of all unemployed (1,124,000 people) have been out of work for more than twelve months, while only 1.5% of them receive the 700 euro/month applicable to the long-term registered unemployed. In the last quarter report for 2016, ELSTAT shows that the amount of Greeks facing long-term unemployment has risen some 146% (from 327,700 to 807,000 people) over the 6-year period. Additionally, there are 350,000 Greek families without a single member working, and unemployment has led some 300,000 highly skilled professionals and workers to leave the country.
[..] According to a study carry out by the Cologne Institute of Economic Research, poverty rate in Greece increased by 40% from 2008 to 2015, the largest increase among EU countries. A new multidimensional poverty index was used to calculate poverty, which is not based on income alone but on other factors such as the deprivation of material goods, quality of education, underemployment and, access to healthcare. In 2015, according to Eurostat, more than one in three residents of Greece experienced conditions of poverty and/or social exclusion. The percentage of those within this group had risen from 29.1% in 2008 to 35.7% in 2015, or 3.8 million people. 21.4% of the Greek population are living below the national poverty line (with an income less than 60 % of the national average), 22.2 % are severely materially deprived,