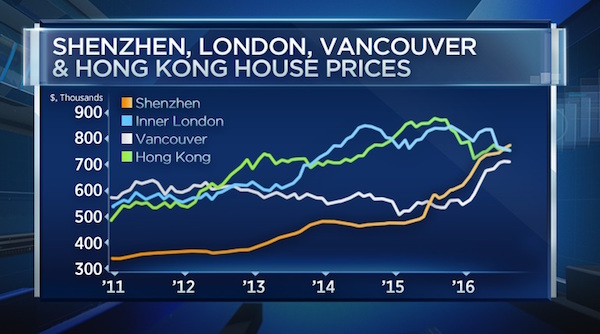
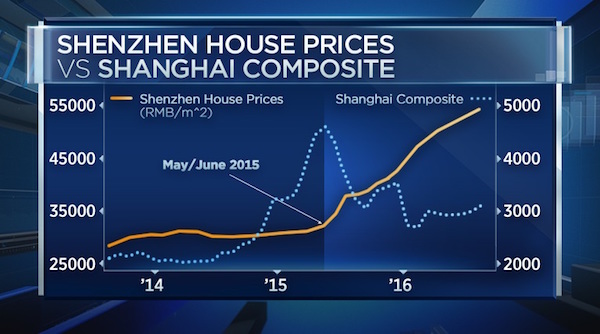
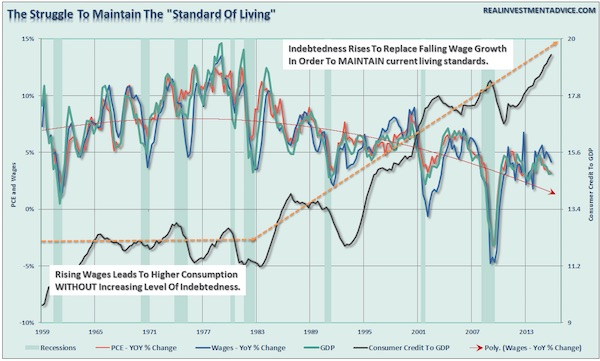
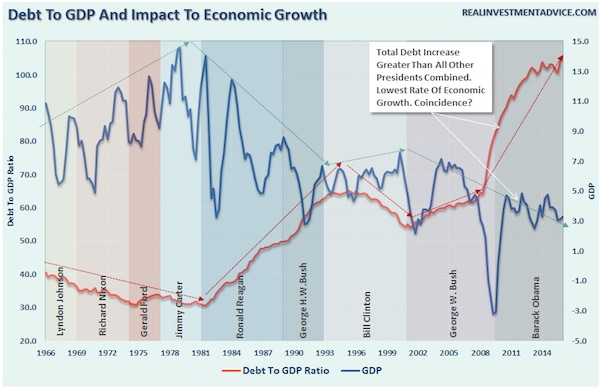
Jack Delano Myrtle Beach, S.C. Air Service Command Technical Sergeant Choken 1943



“..the Fed is pursuing a “weak dollar policy” [..] “They are forcing currency appreciation onto weaker economies. It is irrational..” No, it’s not irrational, but it certainly is short term only. “.. the soaring euro is in the end self-correcting since the eurozone cannot withstand the pain for long..”
• US Dollar Plunges As World Plays Dangerous Game Of Pass The Parcel (AEP)
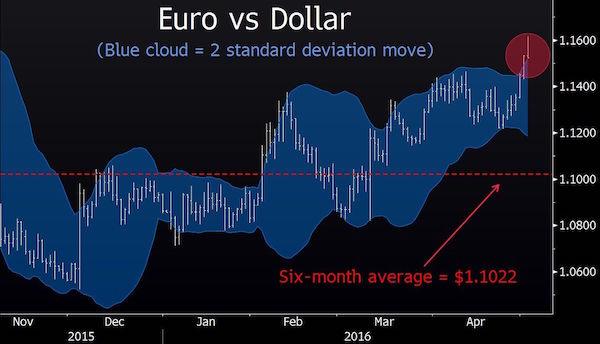
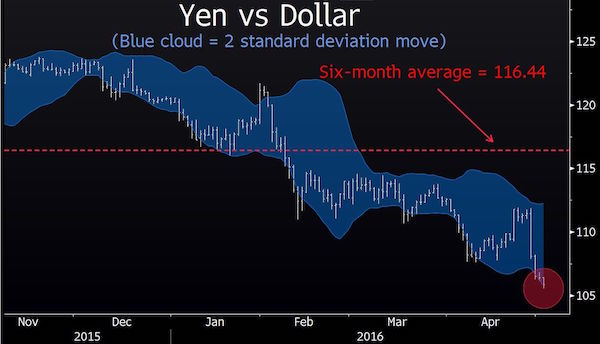
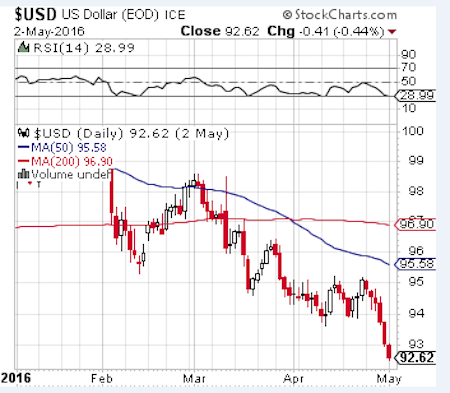
The US dollar has plunged to a 16-month low in the latest wild move for the global financial system, tightening the currency noose on the eurozone and Japan as they struggle to break out of a debt-deflation trap. The closely-watched dollar index fell below 92 for the first time since January 2015, catapulting gold through $1300 an ounce in early trading and setting off steep falls on stock markets in Asia and Europe. The latest data from the US Commodity Futures Trading Commission shows that speculative traders have switched to a net “short” position on the dollar. This is a massive shift in sentiment since the end of last year when investors were betting heavily that the US Federal Reserve was on track for a series of rate rises, which would draw a flood of capital into dollar assets.
Markets have now largely discounted a rate rise in June, and are pricing in just a 68pc likelihood of any increases this year. The dollar slide has been a lifeline for foreign borrowers with $11 trillion of debt in US currency, notably companies in China, Brazil, Russia, South Africa, and Turkey that feasted on cheap US liquidity when the Fed spigot was open, and were then caught in a horrible squeeze when the Fed turned to tap off again and the dollar surged in 2014 and 2015. But it increases the pain for the eurozone and Japan as their currencies rocket. The world is in effect playing a high-stakes game of pass the parcel, with over-indebted countries desperately trying to export their deflationary problems to others by nudging down exchange rates. The Japanese yen appreciated to 105.60, the strongest since September 2014 and a shock to exporters planning on an average of this 117.50 this year.
The wild moves over recent weeks have blown apart the Japan’s reflation strategy. Analysts from Nomura said Abenomics is now “dead in the water”. The eurozone is also in jeopardy, despite enjoying a sweet spot of better growth in the first quarter. The euro touched $1.16 to the dollar early in the day. It has risen over 7pc in trade-weighted terms since the Europe Central Bank first launched quantitative easing in a disguised bid to drive down the exchange rate. Prices fell by 0.2pc in April and deflation is becoming more deeply-lodged in the eurozone economy, with no safety buffers left against an external shock. The European Commission this week slashed its inflation forecast to 0.2pc this year from 1.0pc as recently as November.
There is little that the Bank of Japan or the ECB can do to arrest this unwelcome appreciation. The Obama Administration warned them at the G20 summit in February that any further use of negative interest rates would be regarded by Washington as covert devaluation, and would not be tolerated. “These central banks have reached the limits of what they can do with monetary policy to influence their exchange rates, and this is putting their entire models at risk,” said Hans Redeker, currency chief at Morgan Stanley. “Europe and Japan are operating in a Keynesian liquidity trap. We are nearing a danger point like 2012 when it could lead to an asset market sell-off. We’re not there yet,” he said.
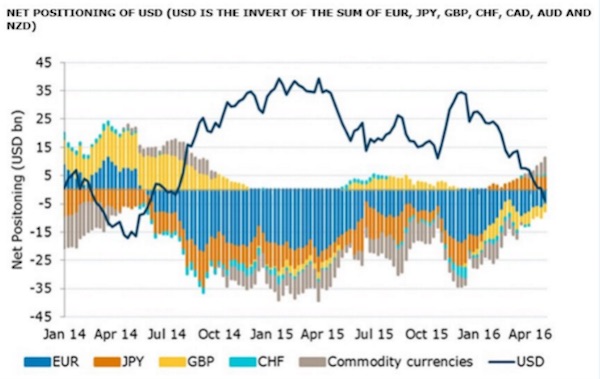
Stephen Jen from SLJ Macro Partners said the Fed is pursuing a “weak dollar policy”, reacting to global events in a radical new way. “They are forcing currency appreciation onto weaker economies. It is irrational,” he said. Yet it may not last long if the US economy comes roaring back in the second quarter a after a soft patch. “I doubt this is really the end of multi-year run for the dollar,” he said. Neil Mellor from BNY Mellon says the soaring euro is in the end self-correcting since the eurozone cannot withstand the pain for long, and as this becomes evident the currency will start sliding again.
Read more …

“Many believe that globalization is largely to blame.”
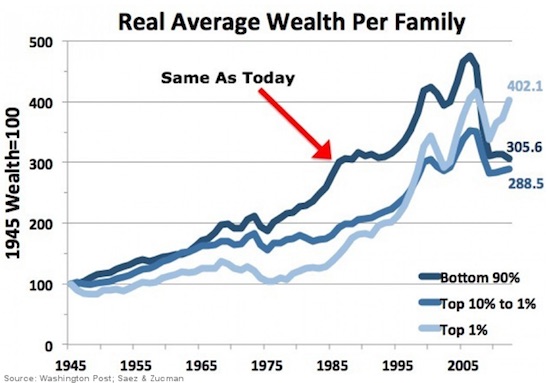
• 90% of Americans Worse Off Today Than in 1970s (VW)
A recent study in March from the Levy Economics Institute found that 90% of Americans were worse off financially in 2015 than at any time since the early 1970s. Furthermore, for the vast majority of Americans, the nation’s economy is in a prolonged stagnation, far worse than that of Japan. Worse than Japan? When we think of the Japanese economy, we think of the “Lost Decades.” Japan’s economy was the envy of the world in the 1980s, but starting in 1991, it fell into a prolonged recession and deflation which lasted from then to 2010. Japan’s GDP fell from $5.33 trillion to $4.36 trillion during that period, which saw wages fall by apprx. 5%. So are we really worse off today than Japan? The Levy Economics Institute at Bard College thinks the answer is YES, when it comes to real income – that is, income adjusted for inflation.
According to their findings, 90% of Americans earn roughly the same real income today as the average American earned back in the early 1970s. As a result of this stagnation in incomes and the plunge in housing values during the Great Recession, 99% of American households have seen their net worth fall since 2007 according to the study. Economic stagnation hasn’t reached the remaining 1% of the US population, which has seen a recovery in their real incomes over the same period to near new highs. The chart below has not been updated to include results for 2015, but the trends are clear. The bottom 99% of US income-earning households have seen their net worth decline since the financial crisis of 2007-2009.
Once upon a time, the American economy worked for nearly everybody, and even the middle class got richer. Things were quite different in the decades preceding the 70s, a period that stretches back to the late 1940s, when real incomes rose for both groups. Simply put, for the vast majority of Americans, the dream of a steady increase in income was lost back in the early 1970s. What can explain this big shift in the income distribution in the last four decades? One clue is in the timeframe of the shift, which coincides with the growing openness of the American economy to international trade and investments. Many believe that globalization is largely to blame.
Read more …

The game is getting dangerous. But it’s the only game in town.
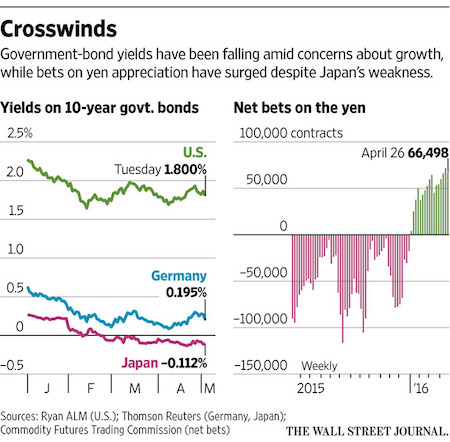
• High Anxiety: Markets Get Roiled (WSJ)
Stocks and oil futures tumbled and Japan’s yen hit its highest intraday level against the dollar since October 2014, as investors struggled to reconcile recent market gains with unease over the pace of global growth. The latest tumult erupted after the Reserve Bank of Australia on Tuesday cut its benchmark rate by one-quarter of a percentage point to 1.75%. The move reflects soft inflation and economic sluggishness driven in part by weak demand from China, the largest buyer of Australian exports. Adding to concerns were a drop in Chinese manufacturing and signals that eurozone growth is slowing more than previously forecast, traders said.
Tuesday’s developments reflect worries that have shadowed a surprising 2016 recovery in the prices of stocks and many commodities. Global growth has slowed this year, prompting major forecasters to cut their outlooks. Yet in recent months the decline of the U.S. dollar and easier policy from global central banks have helped fuel gains in many riskier assets, allowing the Dow industrials to recover from a decline of as much as 10% earlier this year. The action has vexed many portfolio managers and traders, who came into the year expecting the dollar to gain against the yen and euro as the Fed prepared to further tighten its policy and its peers loosened theirs. Instead, both currencies have surged against the dollar.
The dollar fell as low as ¥105.53 during trading Tuesday before retracing to ¥106 later in the session. The dollar traded at ¥120 at the start of the year, according to CQG. The gains threaten to add to economic turmoil in the world’s third-largest economy while deepening investors’ anxiety. “The financial markets are on edge,’’ said Jack McIntyre at Brandywine Global Investment Management. ”Economic growth is still hard to come by.’’
Read more …

Hard to imagine that this still has legs..
• China’s Improbable Commodities Frenzy Leaves Stocks in the Dust (BBG)
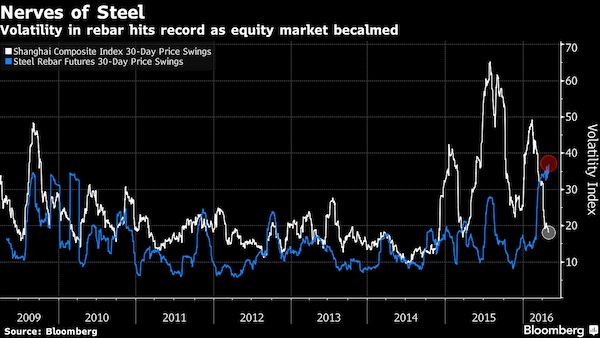
The wild ride in China’s commodity futures is making the nation’s $5.9 trillion stock market look docile. Compared with the stock market, even eggs have been a better investment in China in 2016, with futures climbing 27%. That’s as the cost of a dozen eggs in the U.S. slumped 24% in the first quarter. The epicenter of the commodities boom, however, has been steel reinforcement bars, which have surged 38%. The dizzying increase in speculative activity prompted the head of the world’s largest metals exchange to say that some traders probably don’t even know what they are buying or selling. The Shanghai Composite Index is down 15% this year.
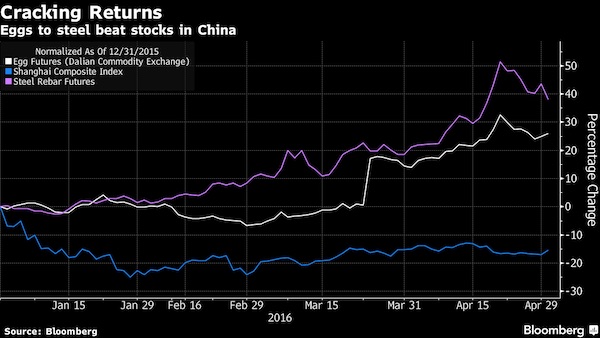
Fluctuations in steel futures have sent a gauge of price swings to the highest level on record. Rebar surged 29% in Shanghai from the end of March through April 22, before dropping about 11%. Bourses in Dalian, Shanghai and Zhengzhou have announced measures to cool the commodities boom including higher fees and a reduction in night hours. Meanwhile, volatility on the Shanghai Composite, which saw gut-wrenching moves over the summer and the start of 2016, has fallen to the lowest level in more than a year as the market turned flat. The intensity of futures trading on Chinese commodities exchanges is making some of the world’s most liquid markets look leisurely. The average iron ore and steel rebar contracts on the Shanghai Futures Exchange are held for less than four hours, compared with almost 40 hours for WTI crude futures on the New York Mercantile Exchange.
Read more …

Time to get out. The House wins.
• Commodities Are China’s Hottest New Casino (FT)
China’s market regulator may have succeeded in taking much of the froth off the country’s surging commodities markets last week, but the message is not filtering down to many dedicated retail traders. As Chinese markets reopened on Tuesday after the May Day holiday, a few dozen young traders in Shanghai crowded into a small room provided by a local brokerage. The mostly 20-something male traders, dressed in jeans and T-shirts, were looking forward to another week of fevered risk-taking in China’s hottest new casino. “It’s better for futures traders to be young because they can learn faster,” said Zhang Jun, 26, who has been trading commodities on the Shanghai Futures Exchange for three years but has only recently begun to make any money.
“This is not relevant to anything you study before you get here. I don’t know anyone who studied a relevant major,” said Mr Zhang, a mechanical engineer by training. On April 29, the China Securities Regulatory Commission ordered the country’s three commodities futures exchanges to curb speculation. The exchanges had already taken steps in that direction, by increasing margin requirements and transaction fees while reducing trading hours. The measures appeared to be aimed primarily at large institutional traders who have contributed to price surges for commodities ranging from steel to eggs, which have increased 50% and 10% respectively over recent months. Liu Shiyu, the CSRC’s new boss, wants to avoid the fate of his recently sacked predecessor, who last year presided over a boom and bust on the Shanghai and Shenzhen stock exchanges.
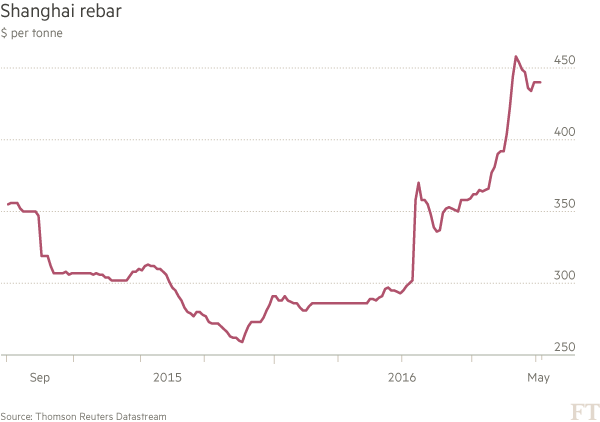
Poor economic data helped Mr Liu’s cause on Tuesday, with the price of the Shanghai exchange’s most popular steel rebar contract falling 4.52% to Rmb2,451 a tonne. Futures for iron ore, the key ingredient in steel production, also took a hit. The most actively traded contract on the Dalian Futures Exchange, which largely trades steel industry inputs, dropped 2.96% to Rmb442.5 per tonne. At the peak of last month’s China commodities fever, the number of steel rebar contracts traded in Shanghai exceeded volumes for the world’s two most important crude oil benchmarks, Brent and West Texas Intermediate.
Read more …

More dangerous by the day, but nothing to stop it.
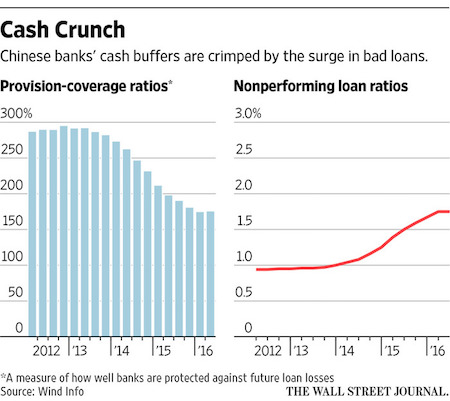
• China’s $1 Trillion In Bad Debt Makes A Sharp Slowdown Inevitable (BI)
The amount of debt being carried in the Chinese economy – mostly by state-owned “zombie” companies – is now so high that it could lead to a financial crisis, according to Macquarie analyst Viktor Shvets and his team. “Unless this vicious cycle is broken, financial crisis or at least a sharp slowdown is an inevitable ultimate outcome,” he wrote in a note to investors on April 29. The China debt problem is simple, at least in concept. To grow its economy, the Chinese government and its central bank have extended credit generously to all sorts of Chinese companies. Many of those are “state owned enterprises,” which are often old-fashioned, uncompetitive, or kept alive by political will rather than economic necessity.
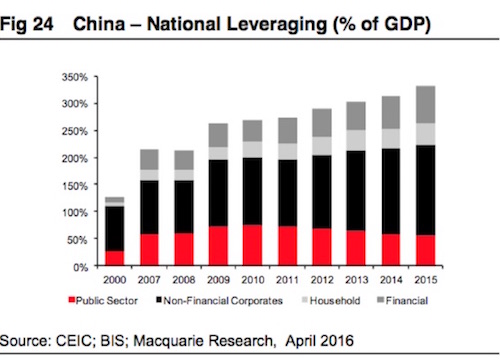
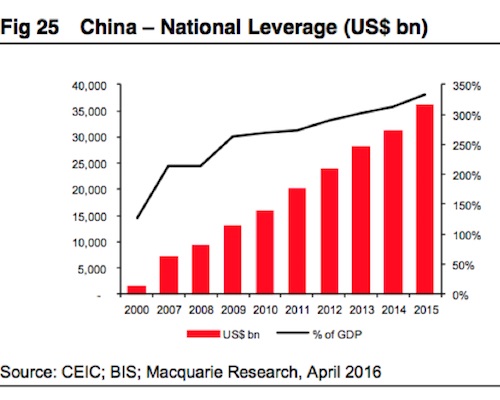
These “zombie” companies exist largely to pay back those debts, but as time goes by some of them default, or fail to pay back all if their loans. This was not much of a problem until recently, Shvets argues, because China’s economy was growing so robustly that it eclipsed the rate of non-performing loans (NPLs). But as the economy has grown, so has its debt, to roughly $35 trillion, or nearly 350% of GDP. If too many companies fail to repay their debts, private lenders and banks will become fearful of lending more. And when that happens, it would plunge China into a financial crisis as liquidity dries up. The size of the debt at risk is so large – and the Chinese economy is such a global driving force – that such a crisis would cause a contagion into the markets of the rest of the world.
Read more …

It can’t be called an accident, but it sure is waiting to happen.
• $571 Billion Debt Wall Points to More Defaults in China (BBG)
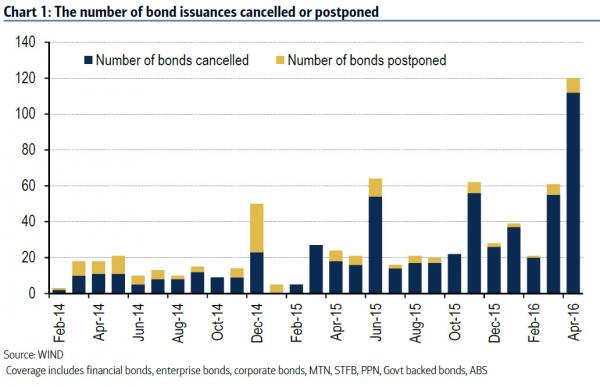
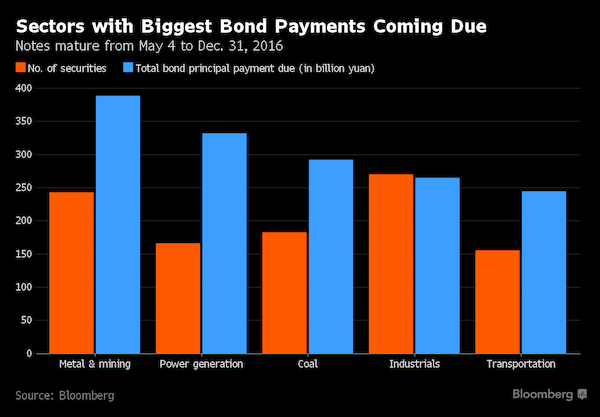
Chinese debt investors are turning bearish at just the wrong time for the nation’s corporate borrowers, which face a record 3.7 trillion yuan ($571 billion) of local bond maturities through year-end. With this year’s biggest note payments concentrated in some of the country’s most-cash strapped industries, China needs buoyant markets to help its companies refinance. Instead, yields in April rose at the fastest pace in more than a year and issuance tumbled 43% as borrowers canceled 143 billion yuan of planned debt sales. Deteriorating investor sentiment has heightened the risk of defaults in a market that’s already seen at least seven companies renege on obligations this year, matching the total for all of 2015.

While government-run banks may step in to help weaker borrowers, missed debt payments by three state-owned firms in the past three months suggest policy makers are becoming more tolerant of corporate failures as the economy slows. “The biggest risk to the onshore bond market is refinancing risk,” said Qiu Xinhong at First State Cinda Fund. “With such a big amount of bonds maturing, if Chinese issuers can’t sell new bonds to repay the old, more will default.”Repayment pressures are most extreme in China’s “old economy” industries, the biggest losers from the nation’s slowdown. Listed metals and mining companies, which generated enough operating profit to cover just half of their interest expenses in 2015, face principal payments of 389 billion yuan through year-end.
Power generation firms owe 332 billion yuan, while maturities at coal companies have swelled to 292 billion yuan. SDIC Xinji Energy, a state-owned coal producer that canceled a bond sale on March 11, must repay 1 billion yuan of notes on May 15, according to Bloomberg-compiled data. China International Capital highlighted the company as one of the riskiest onshore issuers in the second quarter. Fei Dai, SDIC’s board secretary, said Tuesday that the firm will arrange bank loans and other measures to avoid a default. The shares fell 5% to the lowest level since December 2014 in Shanghai on Wednesday. [..] “If you have a large number of companies in high-risk sectors that lose access to financing, there will be defaults or restructuring,” said Raja Mukherji, head of Asian credit research at PIMCO.
Read more …

“China can’t be growing at 6.7% when its export machine has run out of gas..”
• The Global Economy is at Stall Speed, Rapidly Losing Lift (Stockman)
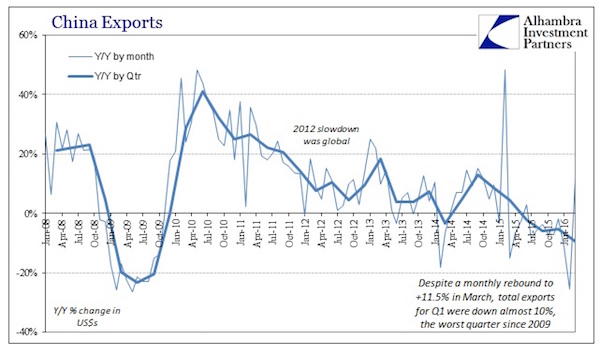
South Korea’s exports tumbled to $41 billion in April, marking the 16th consecutive month of declining foreign sales. Last month’s result represented a 11.2% decline from prior year, and an 18% drop from April 2014. Moreover, within that shrinking total, exports to China were down by 18.4% last month, following a 12.2% drop in March. The Korean export slump is no aberration. The same pattern is evident in the entire East Asia export belt. That’s because the Red Ponzi is in its last innings. Beijing is furiously pumping on the credit accelerator, but to no avail. As can’t be emphasized enough, printing GDP by means of wanton credit expansion does not create wealth or growth; it just results in an eventual day of reckoning when the speculative excesses inherent in central bank money printing collapse in upon themselves.
China is surely close to that kind of implosion. During Q1 total credit, or what Beijing is please to call “social financing”, expanded at a $4 trillion annualized rate. This was up 57% over prior year and represented debt growth at a 38% of GDP annual rate. Stated differently, during the first 90 days of 2016 China piled another $1 trillion of debt on its existing $30 trillion debt mountain, while its nominal GDP expanded by less than $175 billion. That’s right. The Red Ponzi is generating barely $1 of GDP for every $6 of new debt. And much of the “GDP” purportedly generated during Q1 reflected new construction of empty apartments and redundant public infrastructure. By now it ought to be evident that the Chinese economy is a brobdingnagian freak of nature that is destined for a collapse, and that its economic statistics are a tissue of fabrications and delusions.
Even its export figures, which are constrained toward minimum honesty because they can be checked against Chinese imports reported by the rest of the world, are padded to some considerable degree by phony export invoicing designed to hide illegal capital flight. Still, the implication of its export trends are unmistakable. When you put aside the statistical razzmatazz of the Chinese New Year’s timing noise in the data, exports were down by 10% in Q1 as a whole. That is the worst quarterly drop since 2009 amidst the global Great Recession, and was nearly twice the rate of decline during Q4 and Q3 2015. Here’s the thing. China can’t be growing at 6.7% when its export machine has run out of gas, as is so starkly evident in the graph below.
Read more …

Still festering in the dark.
• Fed Expected To Drag Hedge Funds Into Plan To Halt Next Lehman (BBG)
Hedge funds, insurers and other companies that do business with Wall Street megabanks will pay a price for regulators’ efforts to make sure any future collapse of a giant lender doesn’t tank the entire financial system. The Federal Reserve is set to propose so-called stays on derivatives and other contracts that would prevent counterparties from immediately pulling collateral from a failed bank. The plan released Tuesday is meant to give authorities ample time to unwind a firm, hopefully heading off the frantic contagion that spread through markets when Lehman Brothers toppled in 2008. Though the world’s largest banks have already made strides to include such protections in transactions with each other, the Fed’s proposal insists that the shield be expanded to more contracts – including with non-bank firms.
The curbs would apply to any new contract signed by eight of the biggest and most complex U.S. bank holding companies and the U.S. arms of major foreign banks. So, hedge funds and asset managers that want to keep doing business with such lenders would have to comply. Fed Governor Daniel Tarullo said the proposal is “another step forward in our efforts to make financial firms resolvable without either injecting public capital or endangering the overall stability of the financial system.” Industry groups representing firms such as Citadel, BlackRock and MetLife have resisted efforts to rewrite financial contracts, arguing that it abuses investors’ rights and could make things worse by encouraging trading partners to try to pull away from a bank at the first whiff of trouble, even before a failure. But asset managers and insurers would face a tough task in persuading the Fed to change course.
Read more …

Party! It’ll be Britain’s last for a while…
• Barclays Launches First 100% Mortgages Since Crisis (FT)
Barclays has become the first high street bank since the financial crisis to launch a 100% mortgage in the latest sign of a return to riskier lending. The bank is allowing some buyers to take out a mortgage to 100% of the value of the property, without needing a deposit. Most banks require at least a 5-10% lump sum. Barclays said the mortgage only needed to be supported by a family member or guardian, who must set aside 10% of the purchase price in cash for three years in return for interest. It said the new mortgage was designed to remove the issue of borrowers drawing from the “bank of Mum and Dad” to stump up a deposit. Ray Boulger, of broker John Charcol, said: “It is the first true 100% mortgage since the financial crisis.” The move marks a shift back to higher loan-to-value lending reminiscent of the boom times before the crisis of 2008, when 100% mortgages were widely available.
The defunct bank Northern Rock became renowned for its aggressive lending, with its “Together” mortgages offering 125% of the property value. Regulators have since clamped down on risky lending through regulation in 2014, called the Mortgage Market Review, designed to ensure borrowers can repay — although it does not prohibit 100% loans. The Bank of England would also be likely to take a dim view of any widespread return to deposit-free mortgage lending. So far, no other bank has offered such loans. “We haven’t seen a resurgence of 100% mortgages; I don’t think regulation would allow that,” said Charlotte Nelson, of consumer site Moneyfacts. “I don’t think it’s something many other banks will take on. If they’re seen to be lending at 100%, even with a guarantee, it doesn’t look great. Seeing 100% deals back on the market can come off as negative.”
Read more …

The attitude towards whistleblowers still feels medieval.
• Whistleblowing Is Not Just Leaking, It’s an Act of Resistance (Snowden)
“I’ve been waiting 40 years for someone like you.” Those were the first words Daniel Ellsberg spoke to me when we met last year. Dan and I felt an immediate kinship; we both knew what it meant to risk so much — and to be irrevocably changed — by revealing secret truths. One of the challenges of being a whistleblower is living with the knowledge that people continue to sit, just as you did, at those desks, in that unit, throughout the agency, who see what you saw and comply in silence, without resistance or complaint. They learn to live not just with untruths but with unnecessary untruths, dangerous untruths, corrosive untruths. It is a double tragedy: What begins as a survival strategy ends with the compromise of the human being it sought to preserve and the diminishing of the democracy meant to justify the sacrifice.
But unlike Dan Ellsberg, I didn’t have to wait 40 years to witness other citizens breaking that silence with documents. Ellsberg gave the Pentagon Papers to the New York Times and other newspapers in 1971; Chelsea Manning provided the Iraq and Afghan War logs and the Cablegate materials to WikiLeaks in 2010. I came forward in 2013. Now here we are in 2016, and another person of courage and conscience has made available the set of extraordinary documents that are published in The Assassination Complex, the new book out today by Jeremy Scahill and the staff of The Intercept. We are witnessing a compression of the working period in which bad policy shelters in the shadows, the time frame in which unconstitutional activities can continue before they are exposed by acts of conscience.
And this temporal compression has a significance beyond the immediate headlines; it permits the people of this country to learn about critical government actions, not as part of the historical record but in a way that allows direct action through voting — in other words, in a way that empowers an informed citizenry to defend the democracy that “state secrets” are nominally intended to support. When I see individuals who are able to bring information forward, it gives me hope that we won’t always be required to curtail the illegal activities of our government as if it were a constant task, to uproot official lawbreaking as routinely as we mow the grass. (Interestingly enough, that is how some have begun to describe remote killing operations, as “cutting the grass.”)
Read more …

Case in point.
• Whistle-Blower Needed a Smoke Before Giving Up LuxLeaks Data (BBG)
The man who uncovered secret Luxembourg deals that helped companies slash tax rates was actually looking for training documents when he stumbled upon the files on his computer at PricewaterhouseCoopers. On the eve of his departure from the accounting firm in 2010, Antoine Deltour wasn’t fully aware of what he had discovered. He copied the folder and within half an hour had about 45,000 pages detailing confidential tax agreements that became known as the LuxLeaks. Deltour’s discovery triggered the first in a wave of scandals over how thousands of international companies, including Walt Disney, Microsoft’s Skype and PepsiCo, moved money around the globe to avoid taxes. It also landed him in trouble after PwC sued and prosecutors charged him and two other men with theft and violation of business secrets.
“I had discovered gradually the administrative practice of these deals,” Deltour, 30, told a three-judge panel at his trial in Luxembourg Tuesday. “The opportunity to have stumbled over this folder led me to copy it at that moment without a clear goal in mind,” knowing about the “sensitive and highly confidential nature of these files.” Deltour “felt a bit surprised by the volume of the” files and “didn’t immediately do anything with this mass of information,” he told the court. He felt “isolated” and “alone” and unsure of who to turn to. Months later he was contacted by journalist Edouard Perrin, who was working on a documentary about tax practices. The pair met only once, at Deltour’s home in Nancy, France, where Deltour said he needed a moment before handing over the files. “Of course I hesitated,” Deltour told the judge. “I went to smoke a cigarette on the balcony to think a few moments about this.”
The resulting 2012 documentary by Perrin, who is also a defendant in the case, led to interest from the International Consortium of Investigative Journalists. The group put the documents online in 2014, triggering the LuxLeaks scandal. Perrin, 44, another French citizen, was charged in April 2015 with being the accomplice of Raphael Halet, another ex-PwC staffer who is accused of stealing 16 corporate tax returns from the accounting firm and giving them to the journalist. Perrin is also accused of having urged Halet to search for specific documents, a charge both men rejected.
Read more …

Grand Theft Auto. Redux.
• The Kleptocrats’ $36 Trillion Heist Keeps Most of the World Impoverished (DB)
For the first time we have a reliable estimate of how much money thieving dictators and others have looted from 150 mostly poor nations and hidden offshore: $12.1 trillion. That huge figure equals a nickel on each dollar of global wealth and yet it excludes the wealthiest regions of the planet: America, Canada, Europe, Japan, Australia, and New Zealand. That so much money is missing from these poorer nations explains why vast numbers of people live in abject poverty even in countries where economic activity per capita is above the world average. In Equatorial Guinea, for example, the national economy’s output per person comes to 60 cents for each dollar Americans enjoy, measured using what economists call purchasing power equivalents, yet living standards remain abysmal.
The $12.1 trillion estimate—which amounts to two-thirds of America’s annual GDP being taken out of the economies of much poorer nations—is for flight wealth built up since 1970. Add to that flight wealth from the world’s rich regions, much of it due to tax evasion and criminal activities like drug dealing, and the global figure for hidden offshore wealth totals as much as $36 trillion. In 2014 the net worth of planet Earth was about $240 trillion, which means about 15% of global wealth is in hiding, significantly reducing the capital available to spur world economic growth. That $12.1 trillion figure for money looted from poorer countries has been hiding in plain sight. It comes from numbers in the global economic data—derived by comparing statistics from the IMF and the World Bank, supplemented by some figures from the United Nations and the CIA—that do not match up, but which until now no one had bothered to analyze.
You might think that with their vast staffs of economists and analysts the IMF, the World Bank, and other institutions would have run the numbers long ago, but no. Instead, one determined person combed 45 years of official statistics from around the world to calculate the flight wealth for nearly 200 countries that publish comparable economic data. That’s Jim Henry, who was a rising corporate star until he gave it all up to document illicit flows of money and the damage they do to billions of people. Henry has been the chief economist at McKinsey, arguably the world’s most influential business consultancy, and worked directly under Jack Welch at General Electric. A Harvard-educated economist and lawyer, Henry calls himself an investigative economist. His approach is simple: “Just look at the effing data and solve the puzzle” of mismatches between the various official sources.
Read more …

Seems like a bad time to keep on pushing through ever more deals people obviously don’t want.
• France Threatens To Block TTiP Deal (G.)
Doubts about the controversial EU-US trade pact are mounting after the French president threatened to block the deal. François Hollande said on Tuesday he would reject the Transatlantic Trade and Investment Partnership “at this stage” because France was opposed to unregulated free trade. Earlier, France’s lead trade negotiator had warned that a halt in TTIP talks “is the most probable option”. Matthias Fekl, the minister responsible for representing France in TTIP talks, blamed Washington for the impasse. He said Europe had offered a lot but had received little in return. He added: “There cannot be an agreement without France and much less against France.” All 28 EU member states and the European parliament will have to ratify TTIP before it comes into force.
But that day seems further away than ever, with talks bogged down after 13 rounds of negotiations spread over nearly three years. The gulf between the two sides was highlighted by a massive leak of documents on Monday, first reported by the Guardian, which revealed “irreconcilable” differences on consumer protection and animal welfare standards. The publication of 248 pages of negotiating texts and internal positions, obtained by Greenpeace and seen by the Guardian, showed that the two sides remain far apart on how to align regulations on environment and consumer protection. Greenpeace said the leak demonstrated that the EU and the US were in a race to the bottom on health and environmental standards, but negotiators on both sides rejected these claims.
The European commission, which leads negotiations on behalf of the EU, dismissed the “alarmist headlines” as “a storm in a teacup”. But Tuesday’s comments from the heart of the French government reveal how difficult TTIP negotiations have become. France has always had the biggest doubts about TTIP. In 2013 the French government secured an exemption for its film industry from TTIP talks to try to shelter French-language productions from Hollywood dominance. Hollande, who is beset by dire poll ratings, indicated on Tuesday that the government has other concerns about TTIP. Speaking at a conference on the history of the left, Hollande said he would never accept “the undermining of the essential principles of our agriculture, our culture, of mutual access to public markets”. Fekl told French radio that the agreement on the table is “a bad deal”. “Europe is offering a lot and we are getting very little in return. That is unacceptable,” he said.
Read more …

With growth gone, so is the desire for deals. Too much domestic backlash.
• TTIP Has Been Kicked Into The Long Grass … For A Very Long Time (G.)
As talks to broker a global trade deal entered a second tortuous decade, the US and the European Union came up with an idea. Since it was proving impossible to find agreement among the 150 or so members of the World Trade Organisation about how to tear down barriers to freer commerce, they would strike their own agreement. Talks on the Transatlantic Trade and Investment Partnership (TTIP) began in the summer of 2013 with officials in Washington and Brussels confident they could iron out any difficulties by the time American voters decide on who should succeed Barack Obama as president in November this year. This always looked a ridiculously tight timetable and so it has proved. Cutting trade deals is an agonisingly slow process. The last successful global deal – the Uruguay Round – took seven years before being concluding in 1993.
Talks continued on the Doha Round from 2001 until 2015 before terminal boredom and frustration set in. Was it really feasible that TTIP could be pushed through in little more than three years? Not a chance. There are three reasons for that. First, the main barriers to trade between the US and the EU are not traditional tariff barriers, which have been steadily whittled away in the decades since the second world war, but the differing regulatory regimes that operate on either side of the Atlantic. America and Europe have different views on everything from GM food to safety standards on cars so harmonising standards was always going to take a lot of time. Second, the talks have involved controversial issues and have been taking place when trust in politicians and business has rarely been lower. The main driving forces behind TTIP have been multinational corporations and business lobby groups, who stand to gain from harmonised regulations.
With information about the secret negotiations having to be chiselled out by groups hostile to TTIP, voters have drawn the obvious conclusion: the aim of the talks is to enrich big business even if it means playing fast and loose with environmental and health standards. Which leads to the final and most important factor: there are no votes in trade. It would have been no surprise had Angela Merkel voiced strong opposition to the state of the TTIP negotiations, given the level of public antipathy to the trade deal in Germany and her delicate position in the polls ahead of elections next year. Instead, the German chancellor was beaten to it by François Hollande (also facing a showdown with the voters in 2017) who has made it clear he will not sign TTIP in its current form. Years not months of hard slog lie ahead, by which time the US is likely to have a president much less wedded to the idea of striking trade deals. TTIP has just been kicked into the long grass for a very long time, and perhaps for good.
Read more …

Can we have no more of this please?! “The European Commission slapped a 30-year ban on public access to the TTIP negotiating texts at the beginning of the talks in 2013..”
• After The Leaks Showing What It Is, This Could Be The End For TTIP (Ind.)
Today’s shock leak of the text of the Transatlantic Trade and Investment Partnership (TTIP) marks the beginning of the end for the hated EU-US trade deal, and a key moment in the Brexit debate. The unelected negotiators have kept the talks going until now by means of a fanatical level of secrecy, with threats of criminal prosecution for anyone divulging the treaty’s contents. Now, for the first time, the people of Europe can see for themselves what the European Commission has been doing under cover of darkness – and it is not pretty. The leaked TTIP documents, published by Greenpeace this morning, run to 248 pages and cover 13 of the 17 chapters where the final agreement has begun to take shape.
The texts include highly controversial subjects such as EU food safety standards, already known to be at risk from TTIP, as well as details of specific threats such as the US plan to end Europe’s ban on genetically modified foods. The documents show that US corporations will be granted unprecedented powers over any new public health or safety regulations to be introduced in future. If any European government does dare to bring in laws to raise social or environmental standards, TTIP will grant US investors the right to sue for loss of profits in their own corporate court system that is unavailable to domestic firms, governments or anyone else. For all those who said that we were scaremongering and that the EU would never allow this to happen, we were right and you were wrong.
The leaked texts also reveal how the European Commission is preparing to open up the European economy to unfair competition from giant US corporations, despite acknowledging the disastrous consequences this will bring to European producers, who have to meet far higher standards than pertain in the USA. According to official statistics, at least one million jobs will be lost as a direct result of TTIP – and twice that many if the full deal is allowed to go through. Yet we can now see that EU negotiators are preparing to trade away whole sectors of our economies in TTIP, with no care for the human consequences.
The European Commission slapped a 30-year ban on public access to the TTIP negotiating texts at the beginning of the talks in 2013, in the full knowledge that they would not be able to survive the outcry if people were given sight of the deal. In response, campaigners called for a ‘Dracula strategy’ against the agreement: expose the vampire to sunlight and it will die. Today the door has been flung open and the first rays of sunlight shone on TTIP. The EU negotiators will never be able to crawl back into the shadows again.
Read more …

That must be over half the eurozone right there.
• Spain, France, Italy, Portugal To Miss EU Deficit, Debt Reduction Targets (R.)
Three of the euro zone’s four biggest economies look set to break European Union deficit and debt reduction targets this year and next unless they take urgent action, European Commission forecasts showed on Tuesday. The Commission forecast that the three – France, Italy and Spain – were likely to miss goals set for them set by EU finance ministers under a disciplinary procedure for those that run excessive budget deficits and have too high public debt. Portugal would also likely be in breach of EU budget rules. The euro zone’s biggest economy Germany, was in rude fiscal health, the forecasts showed. The Commission’s forecasts, together with medium-term fiscal consolidation plans submitted by governments last month will be the basis for a Commission decision, in the second half of May, on whether to step up the disciplinary procedure against those in breach of the rules.
Read more …

“..for supreme court judges, the right to survive still trumped property rights, a fact that would be considered blasphemy in America..”
• Theft Of Sausage And Cheese By Hungry Homeless Man ‘Not A Crime’ (G.)
Italy’s highest court has ruled that the theft of a sausage and piece of cheese by a homeless man in 2011 did not constitute a crime because he was in desperate need of nourishment. The high court judges in the court of cassation found that Roman Ostriakov, a young homeless man who had bought a bag of breadsticks from a supermarket but had slipped a wurstel – a small sausage – and cheese into his pocket, had acted out of an immediate need by stealing a minimal amount of food, and therefore had not committed a crime. The case, which drew comparisons to the story of Jean Valjean, the hero of Victor Hugo’s Les Misérables, was hailed in some media reports as an act of humanity at a time when hundreds of Italians are being added to the roster of the country’s “hungry” every day, despite improvements in the economy.
One columnist writing in La Stampa said that, for supreme court judges, the right to survive still trumped property rights, a fact that would be considered “blasphemy in America”. But others commented that the case highlighted Italy’s notoriously inefficient legal system, in which the theft of food valued at about €4.70 (£3.70) was the subject of a three-part trial – the first hearing, the appeal, and the final supreme court ruling – to determine whether the defendant had in fact committed a crime. “Yes, you read that right,” an opinion column in Corriere della Sera said, “in a country with a burden of €60bn in corruption per year, it took three degrees of proceedings to determine ‘this was not a crime’.”
Ostriakov, who was described as a homeless 30-year-old from Ukraine, had been sentenced to six months in jail and a €100 fine by a lower court in Genoa, but that punishment was vacated by the supreme court. “The supreme court has established a sacrosanct principle: a small theft because of hunger is in no way comparable to an act of delinquency, because the need to feed justifies the fact,” said Carlo Rienzi, president of Codacons, an environmental and consumer rights group, told Il Mesaggero. “In recent years the economic crisis has increased dramatically the number of citizens, especially the elderly, forced to steal in supermarkets to be able to make ends meet.”
Read more …