Ezra Stoller Parking garage, New Haven, Connecticut 1963

Ponzi’s and zombies. Not Jesse Felder’s original title, but this one by DiMartino Booth is better.
• Zombies In Our Midst (Felder)
To begin to understand the current situation in Minsky terms we must first understand the hypothesis: “The first theorem of the financial instability hypothesis is that the economy has financing regimes under which it is stable, and financing regimes in which it is unstable. The second theorem of the financial instability hypothesis is that over periods of prolonged prosperity, the economy transits from financial relations that make for a stable system to financial relations that make for an unstable system. In particular, over a protracted period of good times, capitalist economies tend to move from a financial structure dominated by hedge finance units to a structure in which there is large weight to units engaged in speculative and Ponzi finance.”
Next we need to understand what these financing units are: “Hedge financing units are those which can fulfill all oftheir contractual payment obligations by their cash flows… Speculative finance units are units that can meet their payment commitments on “income account” on their liabilities, even as they cannot repay the principle out of income cash flows… For Ponzi units, the cash flows from operations are not sufficient to fulfill either the repayment of principle or the interest due on outstanding debts by their cash flows from operations.”
And this is what reminded me of Minsky when I read the recent article in Grant’s with the accompanying chart below. It shows the percent of companies in the S&P 500 that would fall into Minsky’s “Ponzi unit” category. Specifically, Bianco Research defines these “zombies” as companies whose interest expense is greater than their 3-year average EBIT (earnings before interest and taxes). Currently, we face the greatest percentage of “Ponzi units” in at least 20 years.
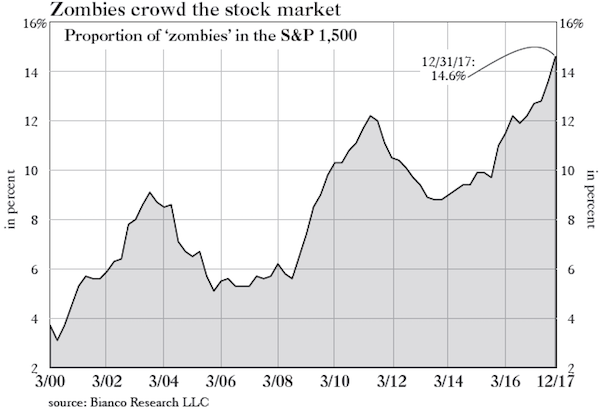
This should be worrisome to investors and even more so to those managing monetary policy because it suggests that financial instability within the economy may be greater than any other time over the past couple of decades. Minsky again: “It can be shown that if hedge financing dominates, then the economy may well be an equilibrium seeking and containing system. In contrast, the greater the weight of speculative and Ponzi finance, the greater the likelihood that the economy is a deviation amplifying system.” Those last three words are critical. “A deviation amplifying system,” simply means an economy built on a virtuous cycle that risks evolving into a vicious one.
So long as interest rates remain low and investor risk appetites remain strong zombies will thrive and the economy will, as well, relatively speaking of course. However, should interest rates rise and risk appetites reverse course the risk of a self-reinforcing downturn grows. Minsky explains: “In particular… if an economy with a sizeable body of speculative financial units is in an inflationary state, and the authorities attempt to exorcise inflation by monetary constraint, then speculative units will become Ponzi units and the net worth of previously Ponzi units will quickly evaporate. Consequently, units with cash flow shortfalls will be forced to try to make position by selling out position. This is likely to lead to a collapse of asset values.”

It won’t be like any of those previous decades.
• After 10 Fat Years For Stock Investors A Lean Decade Is Looming (MW)
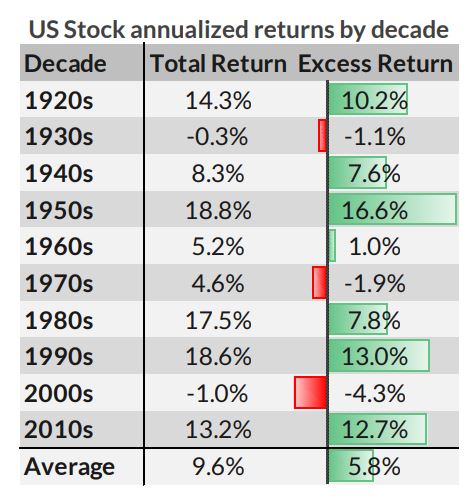
It’s a phrase that comes standard on Wall Street, but which may be taking on ominous undertones in the current market: Past performance is no guarantee of future returns. It should come as no surprise that U.S. equity-market investors have been handsomely rewarded thus far this decade, a period of time that roughly corresponds with the recovery from the financial crisis (the bottom came in March 2009, roughly 10 months before the start of the 2010s). The S&P 500 is up nearly 140% since the start of the decade, and more than 180% on a total-return basis. The Dow Jones Industrial Average is up more than 130% over the same period. Those are obviously strong gains, but even the biggest bulls on Wall Street may not appreciate just how strong this period has been relative to other decades.
“The 2010s have so far been one of the highest-returning and lowest-risk decades for U.S. stocks in the last 100 years,” wrote Howard Wang, co-founder of Convoy Investments. According to Convoy’s data, stocks averaged a total annualized return of 13.2% thus far this decade, comfortably above the long-term average of 9.6%. While this was below four other decades — the best decade was the 1950s, when the average was 18.8%, followed by the 18.6% gain in the 1990s — equities fared better in terms of their excess return above interest rates. By the excess-return measure, the 2010s have seen an average annual return of 12.7%, significantly above the 5.8% long-term average (going back to the 1920s).

“Separately, China’s dollar-denominated trade surplus with the United States rose 19.4% in the first quarter…”
• China Records Rare Trade Deficit In March As Exports Fall 2.7% (R.)
China’s March exports unexpected fell 2.7% from a year earlier, the first drop since February last year, while imports grew 14.4%, more than expected, customs data showed on Friday. That left the country with a rare trade deficit of $4.98 billion for the month, also the first since last February. Analysts polled by Reuters had expected March shipments from the world’s largest exporter to have risen 10.0%, slowing sharply from a 44.5% spike in the previous month which was believed to be heavily distorted by seasonal factors. Import growth had been expected to pick up to 10.0%, after slowing sharply to 6.3% in February.
Analysts expected China would record a trade surplus of $27.21 billion for last month, from February’s surplus of $33.75 billion. For the first quarter, exports rose 14.1%, and imports rose 18.9% on-year. China’s trade performance has got off to a strong start this year, following through on a solid rebound in 2017, thanks to sustained demand at home and abroad. But the export outlook is being clouded by an escalating trade dispute with the United States, which could disrupt China’s shipments and its supply chains, while a cooling property market may curb China’s demand for imported raw materials such as iron ore. Separately, China’s dollar-denominated trade surplus with the United States rose 19.4% in the first quarter.

Ain’t seen nothing yet.
• London House Prices Falling At Fastest Rate In Nine Years (G.)
House prices in London are falling at the fastest rate in nine years, according to Halifax, Britain’s biggest mortgage lender. Prices in the capital were down 3.2% between January and March compared with the previous quarter, the sharpest decline since the depths of the financial crisis, according to regional data collated by IHS Markit and published by Halifax, part of Lloyds Banking Group. London also recorded the sharpest fall in annual house prices since the start of 2011. Property values fell 3.8% in the first quarter from a year ago, following a 0.7% annual drop in the fourth quarter. London prices have been falling on a quarterly and annual basis since the third quarter of 2017.
There was a small annual increase of 0.3% in prices in the south-east of England at the start of the year, and a rise of 1.9% in the south-west. Prices grew strongly elsewhere in the country. The east Midlands and East Anglia recorded the fastest rates of annual price inflation, at 7.3% and 7.2% respectively, followed by Scotland at 6.7% and Yorkshire and the Humber at 6.1%. The standardised price of a home in London was £430,749 in the first quarter, the lowest since the end of 2015. Figures are standardised in order to track the price of a “typical house” by giving values to certain attributes of the properties and using them to calculate the price.

The only game in town.
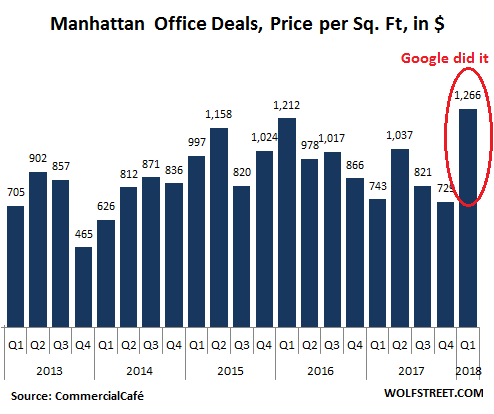
• Google Saves Manhattan Office Market. Chinese Buyers Vanish (WS)
Chinese entities – such as the conglomerates – were once the dominant buyer in US trophy office markets, such as Manhattan. It ended with a big bang in the second quarter of 2017 when Chinese entities accounted for half of the commercial real estate volume in Manhattan, including its sixth largest transaction ever, the $2.2 billion purchase of 245 Park Avenue by the conglomerate HNA Group. It paid $1,282 per square foot, as it was called, “among the highest price per pound for this type of asset.” It was the last big Chinese property purchase in Manhattan.
But Google blew that deal out of the water, with its $2.4 billion acquisition of the iconic eight-story Chelsea Market at 75 Ninth Ave in Q1 this year. This was the second largest deal ever to close in Manhattan. And Google paid a breath-taking $2,181 per square foot. We will never again laugh about the inflated prices Chinese buyers were paying. [..] And here is what that Google deal did to the Manhattan office market: It more than doubled the total volume of sales! Without the Google deal, total transaction volume would have been $2.12 billion. With the Google deal, it jumped to $4.52 billion! [..] the dizzying price of $2,181 per square foot that Google forked over pushed the average price per square foot to a record $1,266, up 70% from Q1 last year:

David is a great ranter.
• The Deep State Closes In On The Donald: Mueller’s War, Part 2 (Stockman)
What is going on in the eastern Mediterranean and over the skies and on the ground in Syria is absolutely nuts; it’s also scary dangerous and utterly unnecessary, too. After all, the imminent Russian/American military clash is over the skeleton of an artificial backwater nation confected in 1916 by two swells in the British and French foreign offices. At length, what was never a nation anyway has finally been reduced to rubble, misery and sectarian fragments. So there is nothing to contest now, and, in fact, there never was. The sovereign government of Syria long ago invited the Russians in and Washington out. Period. Why, then, are commercial aircraft being warned to stay out of Syrian airspace, while the Russian fleet at Tartus scrambles into defensive redeployments?
Likewise, why is the Syrian air force being forced to hide its planes and helicopters in its own country, while Washington steams an armada of warships toward the Mediterranean that is larger and more lethal than the entire Navy of almost every other country in the world? The answer is simple and terrible: Washington has become the War Capital of the planet and now teems with a whole generation of war-obsessed bureaucrats, think-tankers, consultants, lobbyists, militarists, imperialists, neocon belligerents and the legions of military/industrial/spy complex racketeers who feed off a hideously bloated national security budget.
Of course, you also have thousands of politicians—both those now in office and those who hang-around afterwards and get prosperous by hanging-out a shingle to ply the business of operating Washington’s global empire. Among them are the brainwashed, the stupid, the larcenous, the sanctimonious, the venal, the flag-wavers, the sunshine patriots and the ideologues of American exceptionalism, responsibility-to-protect (R2P), democracy propagation and plain old imperial hegemony.

Casino. Not for the faint of heart.
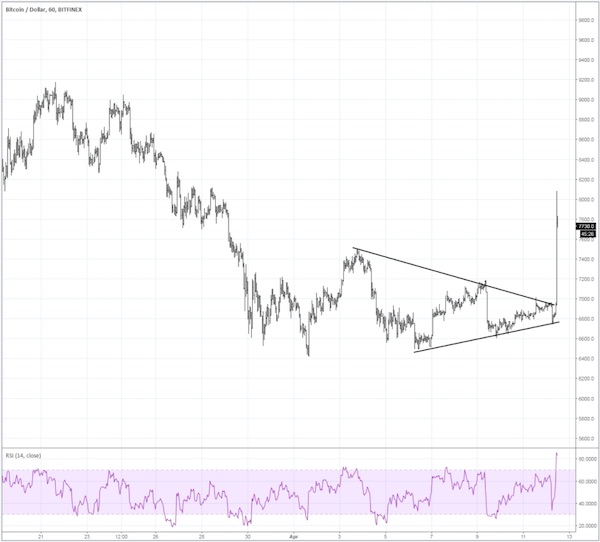
• Bitcoin Surges 15%, Pushing Crypto Market Cap Above $300 Billion (MW)
After a period of low volatility, cryptocurrencies have broken out of their recent ranges, surging to multiweek highs on Thursday. The No. 1 digital currency, bitcoin rose to a two-week peak, trading above $8,000 to an intraday high of $8,055.20, adding as much as 16%. A single coin last changed hands at $7,705.21, up 11%. The intraday move is the largest since Feb. 6 when bitcoin traded down to $5,947.40 before closing at $7,700.39, a 29.4% move. The move comes after bitcoin spent the best part of two weeks in the $6,500 to $7,500 range. The tight sideways action created a so-called wedge formation, which can often presage significant swings in either direction once breached, according to market technicians “We have seen consolidation in a very small range,” said Naeem Aslam, chief market analyst with ThinkMarkets. “When the consolidation is in such a tight range the probability is that a move to the upside can be two to three times the size of the consolidation range.”

Multipolar is the future.
• The US Fading into Irrelevance – A Good Thing for the World (Pieraccini)
As demonstrated by the recent meeting between the defense ministers of Russia and China, the multipolar strategy is now wide-ranging, relegating Washington, Tel Aviv and Riyadh to further digging themselves into the hole they have already dug themselves into (see recent events in Syria with Israel launching 8 missiles and Trump beating the drums of war). As General Wei Fenghe stated, “We came to Moscow to let the Americans know about the close military ties between the armed forces of China and Russia.” When these two military and economic powers unite their efforts, involving regional powers and mediating over various conflicts, it becomes clear that the challenge to Washington’s hegemony is progressively leading away from an international reality consisting of one superpower to one consisting of three to four powers that maintain an international balance via diplomatic, economic and military means.
The phase in which we currently live is turbulent and is essentially caused by a single factor that has two very strong thrusts. The acceleration of the dwindling of the unipolar phase is directly connected with the strategic and tactical errors of the American deep state and its main sponsors, like Israel and Saudi Arabia. At the same time, the opposing push comes from the multipolar environment, which tends to consolidate its sphere of influence via diplomatic and military means. The goal for Moscow and Beijing is to present to the American and European elites a viable alternative that is shared among several actors. For the time being, the Euro-Atlantic establishment continues to consider itself capable of changing the course of events and preventing the drift towards multipolarity.
Whether the Western oligarchy is a victim to its own propaganda or whether it simply wishes to avoid facing reality and is using every means available to postpone an epochal change, is difficult to determine; and this makes the future uncertain, and is therefore highly dangerous.

“The economy may only be operating on a single cylinder, but each time it’s an impressive one.”
• Interest Rate Hikes Are On The Way, But When And How Fast? (AFR)
The Australian economy may not be booming, but it looks to have performed “the miracle pivot”. This is what Ardea Investment Management portfolio manager Tamar Hamlyn calls the economy’s remarkably smooth transition away from a once-in-a-generation mining investment boom without falling into recession. A massive uplift in residential construction activity has carried us through. The “next dance” is infrastructure investment, Hamlyn says. Now we await what feels like another miracle: an RBA rate hike. The economy may only be operating on a single cylinder, but each time it’s an impressive one. We don’t have a solid pick-up in consumption and “we are never going to have that really solid GDP growth until we get that,” Hamlyn says.
But what we are is far from the recessionary fears that were the original rationale for rates at such low levels. It makes sense, then, to think that in the absence of a nasty shock, it seems perfectly reasonable to bet, as RBA governor Philip Lowe flagged again this week, that the next move in rates will be up and not down. But when will that first hike be? And how far will they eventually go? And how quickly will they get there? Accepting that borrowing costs are more likely to get more rather than less expensive is one thing. But anybody trying to assess the potential risks and rewards of taking on a large and long-dated loan obligation, whether it be a mortgage or a business loan, needs to think beyond the next hike. Let’s start with when the RBA will act. Unfortunately, the experts and the market are telling a different story.


Central banks are still supposed to save us. Sure.
• Why Trade Wars Will Unleash Central Banks (Nomi Prins)
You can bet that deep within the halls of the Fed they are developing a game plan to keep the markets from crashing if trade wars escalate. This is another reason to believe that trade wars will be met with cheap money policy. You can look at this as a financial see-saw of sorts. Trade wars, or even media soundbites about them, will spark negative markets reactions. That is why the Fed and other central banks will combat this with cheap words and even cheaper money policies. If the U.S. does jump into a hot trade war it could find itself needing to make up for the costs. The logical place to turn is to the beacon of more money creation from the Fed or to issue more debt.
The Fed would be directly involved in order to keep the cost of debt from rising, again — which is why my analysis forecasts a return to Fed policies that keep rates low. Similarly, other major economies would also unleash their central bank money when needed. This type of tit-for-tat response is already playing out. Beijing has used its new wealth to attract friends, deter enemies, modernize its military, and aggressively assert its central bank into nearly any sector it believes requires assistance. This type of brinksmanship shows that it is only a matter of time before a trade war with China morphs into massive military build-up and competition.

Oh yeah, sure, central bankers will save the planet.
• Global Warming Is a Central Bank Issue (BBG)
Central bankers have been dubbed “masters of the universe” for the tools and powers they have acquired since the financial crisis. Some of them now want to play a more active role in the fight against climate change. Monetary authorities are right to be mindful of the way in which climate risk affects their mandate to ensure price stability and guard financial stability. But that is different from seeking to promote the shift to a “greener” economy, which is the role of government. Last week, central bank governors from the U.K., France and the Netherlands met in Amsterdam to discuss how to adapt regulation to the risks posed by climate change.
Together with five other institutions (from China, Germany, Mexico, Singapore and Sweden), these central banks have formed the “Network for Greening the Financial System” (NGFS). This group has two objectives: sharing and identifying best practices in the supervision of climate-related risks, and enhancing the role of the financial sector in mobilizing “green” financing. The first is entirely reasonable and consistent with the central banks’ traditional role. As Francois Villeroy de Galhau, governor of the Bank of France, said in a speech at the conference, “Climate stability is one of the determinants of financial stability.” It is only right that financial supervisors take an interest in what is going on.
The clearest example concerns the regulation of insurers: Climate change has made extreme weather events such as hurricanes more frequent. Regulators must ensure that the industry updates its models and sets aside enough capital to deal with these growing climate-related risks. To do so, central bankers may need to extend the supervisory horizon beyond their usual time span. Climate change may only pose a threat for the balance sheet some years down the road, but these risks should be assessed now. Villeroy de Galhau argued in his speech that the financial sector should move towards “a compulsory transparency requirement,” so that companies are forced to provide a snapshot of their climate-related risks. It’s an idea supervisors around the world should embrace.

As long as we keep putting species extinction in terms of trade and profit, we are doomed.
• Decline In Bees Puts Supply Of Raw Materials For Global Business At Risk (Ind.)
Businesses face a shortage of raw materials and a drop in the quality of crop as the number of bees decline worldwide, a new report warns. Approximately three quarters of crops around the world depend on pollination, all of which could soon be threatened as more than a third of wild bee and butterfly species face extinction, according to a joint study by the UN, the University of East Anglia and Cambridge University. Major businesses, including Asda, the Body Shop, Mars and Pepsico, say they are unable to take action largely because of uncertainty around which crops and regions are vulnerable to the decline in pollinators such as bees.
“The role pollinators play – be it tiny midges for cocoa or squirrels for coconut – is not well understood and can be taken for granted,” says Jos van Oostrum, director of sustainable solutions at chocolate and confectionary maker Mars. Cocoa, a vital ingredient in the production of chocolate, is at particular risk from a declining number of bees and other species that help spread pollen. The risks of a shortfall in raw materials not only prove a challenge for food production, but also the sourcing of ingredients for beauty products. “The importance of pollination for natural raw materials is increasingly a priority for us,” said the Body Shop’s sustainable sourcing manager Francesca Brkic.

Everytime I make a new friend I find out they’re about to die. It’s making me terribly sad.
• No Plan To Protect Queensland’s Green-Haired Turtle From Extinction (G.)

The Australian government does not have a plan to save an endangered Australian turtle species that received global attention on Thursday for its green mohawk and its ability to breathe through its genitals. The Mary river turtle, found only in that one river in Queensland, attracted worldwide headlines as one of the standout species on a new list of the most vulnerable reptile species compiled by the Zoological Society of London (ZSL). But despite this listing it does not have a national recovery plan to protect it from extinction and it is unclear whether any federal government funds have been specifically allocated for its protection. The turtle is 29th on ZSL’s Evolutionary Distinct and Globally Endangered (Edge) list for reptiles, which highlights the conservation needs of some of the world’s unique reptiles.
The turtle is not the only reptile species found in Australia to appear on the list, with eight species making the top 100, and seven of those appearing in the top 40. Among them are the critically endangered western swamp tortoise, which is number seven on the Edge list, the pig-nosed turtle, number 19 on the list, and the Gulbaru Gecko, a critically endangered Queensland species that was only discovered in 2001 and appears at 40 on the list. Conservationists say the list highlights the lack of conservation attention many Australian reptiles receive compared to more charismatic and iconic mammal and bird species. The federal government’s threatened species strategy specifically targets 20 mammals, 20 birds and 30 plants, but no reptiles.

The climate on both sides of the Atlantic would change too much to imagine.
• Gulf Stream Slowdown ‘About A Century Ahead Of Schedule’ (TP)
New research provides strong evidence that one of the long-predicted worst-case impacts of climate change — a severe slow-down of the Gulf Stream system — has already started. The system, also known as the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), brings warmer water northward while pumping cooler water southward. “I think we’re close to a tipping point,” climatologist Michael Mann told ThinkProgress in an email. The AMOC slow down “is without precedent” in more than a millennium he said, adding, “It’s happening about a century ahead of schedule relative to what the models predict.”
The impacts of such a slowdown include much faster sea level rise — and much warmer sea surface temperatures — for much of the U.S. East Coast. Both of those effects are already being observed and together they make devastating storm surges of the kind we saw with Superstorm Sandy far more likely. The findings come in two new studies published this week. One study published in the journal Nature, titled “Observed fingerprint of a weakening Atlantic Ocean overturning circulation,” was led by the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research. It finds that the AMOC has weakened “around 15 per cent” since the mid-twentieth century, bringing it to “a new record low.”