Leonardo da Vinci A Copse of Trees 1508

September’s a long way away.
• Trump: US “Needs A Good Shutdown In September To Fix This Mess” (ZH)
With Congress poised this week to approve a deal to fund the government through September, the first major bipartisan legislation of Trump’s presidency, after lengthy negotiations (which have appeared to signal numerous ‘folds’ by President Trump), apparently frustrated by the lack of tryannical powers that a simple majority grants him, President Trump has lashed out this morning at disagreeable Democrats, and in particular Senate Democrats. As a reminder, the proposed government funding deal does not include funding for Trump’s proposed wall along the U.S.-Mexico border or include language stripping federal money from so-called sanctuary cities, both of which the White House demanded at the outset of negotiations. In fact, as we reported yesterday, the bill has been seen widely as a victory for Democrats, something which has been panned by the conservative press.
While the White House also backed off a threat to withhold ObamaCare subsidy payments to insurance companies, Trump did secure increased military spending in the 2017 budget deal. According to the Hill, the comments are likely irk top Republican lawmakers, who have been frustrated by Trump’s repeated attempts to intervene in the legislative process. The businessman-turned-president, in turn, has vented frustration with the slow pace of work on Capitol Hill. “I’m disappointed that it doesn’t go quicker,” Trump told Fox News last week when asked about the Republican effort to repeal and replace ObamaCare. Commenting on Trump’s tweets, Citi asks rhetorically whether “this could be a case of cutting one’s nose to spit one’s face? – Potentially problematic when the nose in question is attached to the current administration… It seems counterintuitive that a sitting president would want a shutdown, unless he was to blame it on the opposition in order to force through reform/encourage a voter backlash.”
Bloomberg reports that “The message appeared to encourage the Republican-controlled Senate to change rules that now require 60 votes to end a filibuster of legislation. Republicans reduced the threshold to 51 votes for Supreme Court nominees this year and could do the same for legislation with a simple majority vote.” USD does not seem to have reacted to the President’s tweet (it can’t every time, after all), which may just be more political manoeuvring rather than a signal of intent. In any case, we’re not so sure there is such a thing as a “good” shutdown of the US government – and with what will be over $20 trillion in debt and a declining GDP by that time, one wonders which ratings agency will have the balls to downgrade the world’s reserve currency this time?

“Someone will buy it for a dollar because they want to get the loan book [..] it goes for a lot less than it’s trading at today.”
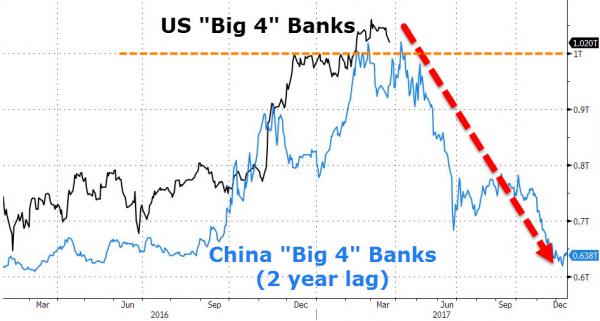
• Home Capital Fails to Draw Buyout Interest From Canada Banks (BBG)
Canadian banks and financial firms are so far showing little interest in buying Home Capital, vindicating short-sellers who say the embattled mortgage lender could be sold off piecemeal, driving the stock down further. “People in the industry would rather see these guys go out of business because the loans aren’t worth the risk, and they’re so leveraged,” said Marc Cohodes, a private investor and part-time chicken farmer in California who has been shorting the stock, or betting on declines, for more than two years. Home Capital’s rival Equitable joined a list of companies that have said they aren’t interested in taking over the struggling mortgage lender, which hired investment banks last week for a possible sale after the stock plunged by two-thirds amid a regulatory probe.
“The bottom line is no,” Equitable Chief Executive Officer Andrew Moor said on Monday. “We have some concerns based on what we’ve read about how they underwrote their loans and their internal controls.” Other banks have indicated that they aren’t interested. Canadian Western Bank CEO Chris Fowler said his Edmonton, Alberta-based lender, which has an alternative mortgage business, would not be a buyer for all of Home Capital. He added the bank will consider “selectively” acquiring loan portfolios. A Laurentian Bank of Canada spokeswoman said that for the lender to be interested in an acquisition it needs to be financially sound and a good strategic fit. Laurentian is active in the alternative lending space.
Canada’s biggest commercial banks, meanwhile, are unlikely to be interested because Home Capital’s mortgages are with customers who wouldn’t qualify for a loan with them, said Sumit Malhotra, an analyst at Bank of Nova Scotia, in a research note. They might be interested in the loan book, he added. [,,] Other short sellers agree with Cohodes. Jerome Hass at Lightwater in Toronto, said he wonders why anybody would buy Home Capital when they could just pick up the mortgages. “It’s got all this litigation against it, it’s going to have all these liabilities against it, so why not just take their loan book off their hands?” Hass said in an interview. “Someone will buy it for a dollar because they want to get the loan book, but I don’t see it going for much, and it goes for a lot less than it’s trading at today.”

No purchasing power.
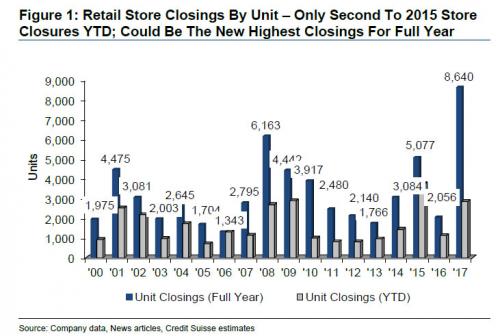
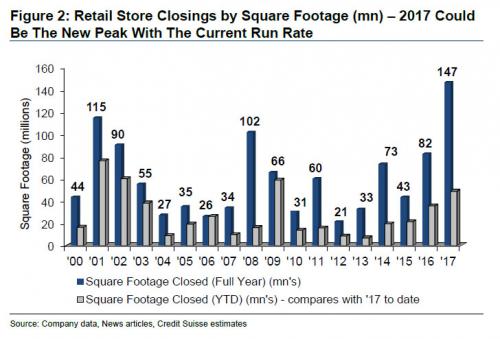
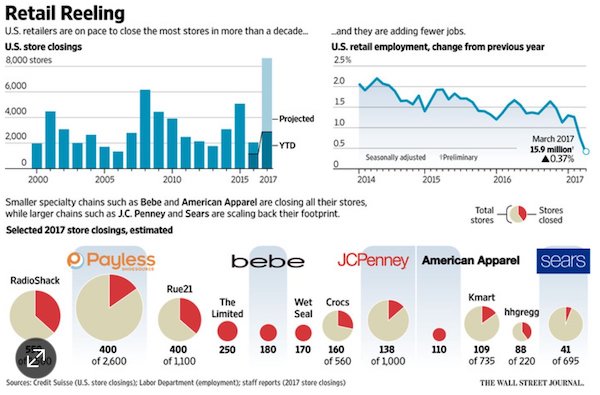
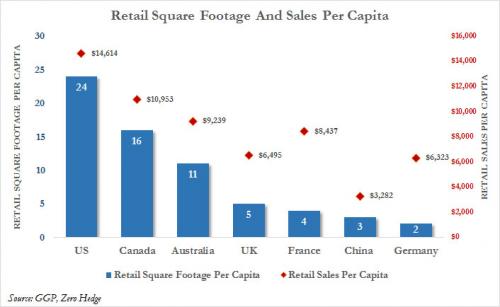
• Hot Air Hisses out of US Auto Bubble (WS)
A 4.7% drop in sales, bad as it is, wouldn’t qualify for #carmageddon. These things happen. But here’s the thing: Automakers had shelled out $3,465 in incentives per new vehicle sold, on average, according to TrueCar estimates. A record for the month of April. It beat the prior record of $3,393, set in April 2009. It amounts to about 10% of suggested retail price, similar to March. The last period when incentive spending was at this level of MSRP was in 2009 as the industry and sales were collapsing. The #carmageddon point to watch: despite the 13.4% year-over-year surge in incentive spending to nearly $5 billion, total vehicle sales fell 4.7%! When these massive incentives fail to even slow the sales decline, serious problems lurk beneath the surface. This table shows the largest automakers, their year-over-year sales performance – the sea of red ink – along with average per-unit incentive spending and total incentive spending:
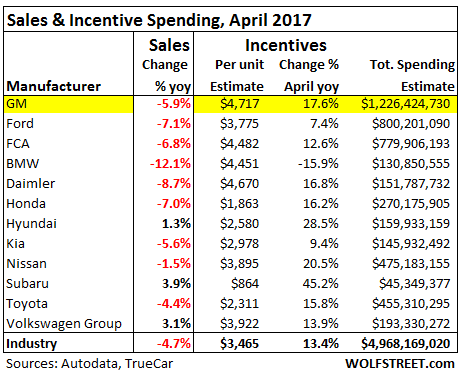
GM shelled out the most incentives on average per vehicle, in total $1.23 billion. In March, it had spent about $1.3 billion. At this rate, GM is spending just under $4 billion per quarter in incentives. By comparison, in its Q1 earnings, GM reported “North America” revenue of $29.3 billion. At this rate, it is spending about 13% of its North American revenues on US incentives. But it’s just not working out. Total sales dropped nearly 5.9%, to 244,200 units, with car sales plunging 12.5% and even truck sales falling 3.2%. A gruesome detail: Silverado-C/K pickup sales plunged 20% to 40,154 units. Total retail sales (not including fleet sales) fell 4% to 191,911 vehicles. GM ended the month with 100 days’ supply, up from the nail-biter level of 98 days at the end of March.

The UK is so divided along multiple fault lines that May has nothing, unless she’s prepared to walk away.
• May’s Election Fighting Talk Fuels Brexit War of Words With EU (BBG)
U.K. Prime Minister Theresa May vowed she won’t be pushed around in Brexit talks with the European Union as her war of words with Brussels escalates before negotiations even begin. The premier said European Commission President Jean-Claude Juncker is learning she can be “bloody difficult” after leaked details of a dinner meeting between the leaders alleged he was shocked by her approach to negotiating Brexit. May won a measure of support from several European government officials, who distanced themselves from Juncker’s apparent skepticism about the chances of a Brexit deal. The row blew up after details of the allegedly disastrous meal Juncker attended at May’s London residence last week were reported by a German newspaper.
“What we’ve seen recently is that at times these negotiations are going to be tough,” May told BBC television in an interview Tuesday. “During the Conservative Party leadership campaign, I was described by one of my colleagues as a bloody difficult woman. And I said at the time the next person to find that out will be Jean-Claude Juncker.” The clash between London and the European Commission comes as May seeks re-election on June 8 in a campaign defined by Brexit, and the argument won’t necessarily hurt her chances. While EU officials are concerned about such a public dispute ahead of negotiations, it could help May’s Tories convince voters the U.K. needs what she calls her “strong and stable leadership” for the Brexit talks.
May claims her main rival for power, opposition Labour party leader Jeremy Corbyn, would be too “weak” to succeed at the negotiating table. Germany’s Frankfurter Allgemeine Sonntagszeitung newspaper said on Sunday that Juncker left a dinner on April 26 “10 times more skeptical” of reaching a Brexit deal. In her interview on the campaign trail, May told the BBC she hopes to agree an accord that works for the U.K. and the EU, saying there’s “a lot of similarity” between her proposals and the bloc’s negotiating guidelines.

Can a national currency exist alongside a European one?
• Le Pen Wants A French National Currency Within Two Years After Election (R.)
Far-right presidential challenger Marine Le Pen said capital controls could be used if she won the election and there was a run on banks as she negotiated France’s exit from the European Union, but stressed they were unlikely to be needed. In an interview with Reuters ahead of Sunday’s decisive second round, Le Pen reaffirmed she wanted to take France out of the euro and said she hoped the French people would have a national currency in their pockets within two years. Le Pen said she wanted to replace the EU single currency with another, looser type of cooperation in the form of the ECU basket of currencies that preceded the euro. That would exist alongside a national currency.
“The objective is to transform the euro ‘single currency’ into a euro ‘common currency’, going back to the ancestor of the euro, the ECU, which was an accounting unit that did not stop each country from having each its own currency,” Le Pen said. Calling the euro a deadweight on the French economy, the National Front candidate said a new national currency would better protect French people’s savings. She accused the “establishment” of wanting to “frighten” voters into thinking otherwise. “I am convinced there won’t be any banking crisis,” Le Pen said when asked if French negotiations to quit the EU could trigger a run on French banks.
Asked if she would impose capital controls if savers nevertheless did rush to take their money out of banks, she said: “If there’s a run on banks, we could very well imagine such a solution for a few days, but I’m telling you it won’t happen.” Le Pen said she would launch negotiations over reforms of the EU immediately after winning, saying this would allow France to regain national sovereignty. The talks would include ditching the euro as well as regaining control of France’s borders and being able to decide French legislation alone, she said. Those negotiations could last six to eight months, she said, after which France would hold a referendum on its EU membership.

Whatever happens in Sunday’s 2nd round, a mess is certain.
• Macron Victory Could Mark The Start Of Political Upheaval For France (CNBC)
France’s political course is likely to remain far from certain even with a win for presumed victor Emmanuel Macron, as his inability to form a parliamentary majority threatens to undermine his authority both domestically and across Europe, political analysts have suggested. Sunday’s second round runoff will mark the start of a period of tension for the country as the successful candidate waits to see if they can garner a large enough parliamentary majority in June’s legislative election to enact change, Dominique Reynié, professor of political science at the Sciences Po institute in Paris, told CNBC Tuesday. “I’m not worried about Macron’s ability to win, but the question surrounds what kind of turnout he will achieve and what his ability to gain a majority in the June election will be,” explained Reynié.
Polls are currently pitching centrist Macron to gain anywhere from a 59% to a 64% lead on his far-right opponent Marine Le Pen. However, this lead will do little to boost Macron’s authority in government, Reynié suggests. The independent will have to gain significant support from other parties if he is to form a majority when France once again heads to the polls on June 11 and June 18 to elect the 577 members of its National Assembly. “It will all depend on his margin of victory. A 55 to 45% win for Macron would be a disaster. Even 60 to 40 is not at all a triumph; a 20% margin would be very difficult. “It would be a crisis. It is not normal and would be a problem both on the streets of France and for Europe,” said Reynié.
In the first round of voting, Macron’s En Marche!, or Onwards! party, achieved a majority in 240 constituencies versus Le Pen’s 216. However, Reynié says this is simply not enough. “The smaller Macron’s majority the harder it will be for him to win the general election in June. He needs support; it is not possible to have power as President without support. “This could cause parliament to be largely fragmented like in the first round, with discussions taking place in fractured groups. Macron will have to negotiate with MPs and will be fragile and unpopular.”

Has been for years.
• Italy Is Europe’s Next Big Problem (BBG)
Emmanuel Macron looks on course to become France’s new president, ending the threat of a euroskeptic at the Elysee. Even if Macron wins, though, it’ll be too soon to celebrate a new phase of stability in the euro zone. Across the Alps, an economic and political storm is brewing – and there’s no sign anyone can stop it. Italy’s economic problems are in many ways worse than France’s. Public debt stands at nearly 133% of gross domestic product; in France, it’s 96%. The last time Italy grew faster than France was in 1995. Both countries have struggled to stay competitive internationally – but French productivity has risen by roughly 15% since 2001, whereas Italy’s has stagnated.
Meanwhile Italian politics goes from bad to worse. The Five Star Movement, a populist force that wants to hold a referendum on Italy’s membership of the euro system, is riding high in the polls and currently neck and neck with the center-left Democratic Party. The general election, scheduled for next spring, is unlikely to produce a clear winner – and there’s even a small chance it may result in a Eurosceptic government, if the Five Stars were to win enough votes and form an alliance with the fiercely anti-euro Northern League. Europhiles in Italy are busily looking for an Italian Macron – someone who could offer a liberal remedy for Italy’s economic woes while fighting off the threat of “It-exit.” Investors would like that. In the autumn, the European Central Bank looks set to slow its purchases of government debt. The prospect of political instability in Rome could spook investors, raising doubts over the sustainability of Italy’s debt.
In many ways, Matteo Renzi, Italy’s former prime minister, who resigned after a heavy defeat in December’s constitutional referendum, would be the obvious choice. At 42, he is only three years older than Macron. He too has sought to modernize the left, even though he preferred to climb through the ranks of his party, rather than set up a new one as Macron did. The trouble is that Renzi looks increasingly like a spent force. He has just obtained a fresh mandate as party leader, but many Italians doubt his promises because he reneged on a pledge to quit politics if he lost the referendum. His message has also become muddled. He claims to be pro-EU, but never misses a chance to bash Brussels – for imposing fiscal austerity, especially. Why should voters opt for Renzi’s half-hearted euroskepticism when they can have the real thing?

“Money does not give you the right to fund revolutions to recast the world in your image.”
• Soros At it Again – Trying to Overthrow Polish Government? (Martin Armstrong)
QUESTION: Mr. Armstrong, I attended your March 1999 conference in Tokyo when I worked for ___ bank. I remember you called out Soros and crew and said they were trying to manipulate the yen for fiscal year end. You warned the Japanese how to defeat the Club. If I remember, he and his crew lost $1 billion when everyone in Tokyo followed your advice. Many assumed what they did to you 6 months later was retribution. Now he is at it in Poland funneling money he made from such trading in through Norway to create political unrest. What is it with this guy? Why does he play God?
ANSWER: Oh yes. I remember that event very clearly. That’s why they started calling me Mr. Yen because it was me and our clients against the Club and the Club lost. They were trying to push the yen down for the fiscal year-end roll of March 31st and then run it up into April 1st. They had our clients lock it in and that forced the manipulators out. That was a wild day – 3 big figures in a single day in an outside-reversal was a big move back then. I know the rumor was that Soros was in on that and the Club lost $1 billion. Not sure how much they lost on that one. It was the good-old fun days of confrontations. The Polish government wants to stop the distribution of Norwegian money flowing into Poland coming from Soros’ funded Batory Foundation, which manages over 800 million euros with a target of overthrowing the Polish government by 2020.
Since 2014, the Batory Foundation has distributed some 130 million zlotys (around 31.7 million euros) to various associations and organizations within Poland to change the government. According to Bloomberg, this includes organizations for the promotion of parliamentary democracy , but only if it agrees with Soros agenda. Effectively, Soros is trying to defeat ‘Catholic values’ in Poland which are supported by the population and government. [..] Soros has publicly stated he does not believe in God. Many who worked for him said they think he believes he is a god with the right to reshape the world in his image. So have many throughout history and they are responsible for the murder of countless millions. Money does not give you the right to fund revolutions to recast the world in your image.

Merkel knows Putin can’t give in on Ukraine. Useless rhetoric.
• In Tense Encounter, Merkel Tells Putin Sanctions Must Remain (BBG)
German Chancellor Angela Merkel told President Vladimir Putin that EU sanctions will have to remain on Russia as the two leaders clashed over Ukraine, human rights and election meddling at a chilly encounter in the Black Sea city of Sochi. Addressing a joint press conference with Putin after about two hours of talks on Tuesday, Merkel raised concerns about the rights of homosexuals in Chechnya and Russia’s role in the war in Syria. She devoted much of her time to the lack of progress in resolving the three-year-old conflict in Ukraine. While Putin sought to lay the blame on the Ukrainian government, the chancellor said that a cease-fire is required as part of the “arduous” so-called Minsk process for restoring peace in eastern Ukraine and appealed to him to make it happen.
“My goal remains to get to the point where we can lift EU sanctions, but there’s a link here,” Merkel told reporters on her first visit to Russia since May 2015. The peace process is “moving very slowly, we only make progress in small steps and constantly have setbacks.” Merkel, who met with President Donald Trump at the White House in March, is visiting Putin in her capacity as holder of the presidency of the Group of 20 nations. As well as Ukraine, Merkel and Putin discussed the civil war in Syria and the G-20 summit in Hamburg in July, when the Russian and U.S. presidents are scheduled to meet for the first time. Ukraine was the main flashpoint, with Putin reiterating his stance that the Russian-backed breakaway regions in southeastern Ukraine split off because of a “coup d’etat, an unconstitutional change of power in Kiev.”
Merkel noted the two leaders’ “different opinions” about the origins of the conflict in Ukraine, which spiraled after protests over a scrapped accord with the EU triggered the downfall of the Russian-backed government in 2014. “We don’t share this view,” Merkel said in the briefing, which dispensed with the usual pleasantries or leaders’ banter. “We think that the Ukrainian government came to power through democratic means.” Although she’s among Putin’s sternest critics, Merkel has sought to keep a channel open to the Russian leader even as she holds the line on EU sanctions, which are a response to Russia’s annexation of Crimea and backing for Ukrainian separatists. Hours before Putin was scheduled to speak by phone with Trump on Tuesday, he responded again to allegations of electoral interference, saying “we never interfere in the political life of other countries.”

There are people with less bias on Putin. Just not in US or EU politics.
• ‘It’s Very Important We Hear What Putin Has To Say’ – Oliver Stone (RT)
The man behind three films about American presidents, Oliver Stone, says his upcoming feature about Russian President Vladimir Putin “opens up a whole viewpoint that we as Americans haven’t heard,” and could help prevent “a dangerous situation – on the brink of war.” Academy Award-winning director and revered documentary filmmaker Stone said in interview with the Sydney Morning Herald that his new film about Putin will be released soon. “It’s not a documentary as much as a question and answer session,” he said. “Mr. Putin is one of the most important leaders in the world and in so far as the United States has declared him an enemy – a great enemy – I think it’s very important we hear what he has to say.” The film will present Putin’s viewpoint of political events since he was first elected president of Russia in March 2000.
“It opens up a whole viewpoint that we as Americans haven’t heard,” Stone told the newspaper, adding that his crew went to see the indefatigable Russian leader four times over the course of two years. “I talked to him originally about the Snowden affair, which is in the film. And out of that grew, I think, a trust that he knew that I would not edit it so much,” he said, adding that Putin “talks pretty straight.” “I think we did him the justice of putting [his comments] into a Western narrative that could explain their viewpoint in the hopes that it will prevent continued misunderstanding and a dangerous situation – on the brink of war.” The 70-year-old director also commented the accusations of Russian influence on the US presidential elections.
“That’s a path that leads nowhere to my mind. That’s an internal war of politics in the US in which the Democratic Party has taken a suicide pact or something to blow him up; in other words, to completely de-legitimize him and in so doing blow up the US essentially. “What they’re doing is destroying the trust that exists between people and government. It’s a very dangerous position to make accusations you cannot prove,” he added. Stone also said he does not believe claims circulating in the mainstream media that Moscow allegedly passed some classified documents to WikiLeaks in a bid to influence the November US elections. “I hold Assange [WikiLeaks editor Julian Assange] in high regard in many issues of state. I take very seriously his statement that he received no information from Russia or any state actors,” Stone said.

“.. it is French and German taxpayers who will pay the price when the Greek debt is inevitably written off.”
I should get the book later this week.
• Adults in the Room – One Of The Greatest Political Memoirs Ever (Mason)
Varoufakis began on the outside – both of elite politics and the Greek far left – swerved to the inside, and then abruptly abandoned it, after he was sacked by his former ally, Greek prime minister Alexis Tsipras, in July 2015. He dramatises his intent throughout the crisis with a telling anecdote. He’s in Washington for a meeting with Larry Summers, the former US treasury secretary and Obama confidant. Summers asks him point blank: do you want to be on the inside or the outside? “Outsiders prioritise their freedom to speak their version of the truth. The price is that they are ignored by the insiders, who make the important decisions,” Summers warns. Elected politicians have little power; Wall Street and a network of hedge funds, billionaires and media owners have the real power, and the art of being in politics is to recognise this as a fact of life and achieve what you can without disrupting the system.
That was the offer. Varoufakis not only rejected it – by describing it in frank detail now, he is arming us against the stupidity of the left’s occasional fantasies that the system built by neoliberalism can somehow bend or compromise to our desire for social justice. In this book, then, Varoufakis gives one of the most accurate and detailed descriptions of modern power ever written – an achievement that outweighs his desire for self-justification during the Greek crisis. He explains, with a weariness born of nights in soulless hotels and harsh-lit briefing rooms, how the modern power network is built. Aris gets a loan from Zorba’s bank; Zorba writes off the loan but Zorba’s construction company gets a contract from Aris’s ministry. Aris’s son gets a job at Zorba’s TV station, which for some reason is always bankrupt and so can never pay tax – and so on.
“The key to such power networks is exclusion and opacity,” Varoufakis writes. As sensitive information is bartered, “two-person alliances forge links with other such alliances … involving conspirators who conspire de facto without being conscious conspirators”. In the process of telling this story, Varoufakis not only spills the beans but beans of the kind the Greeks call gigantes – fat ones, full of juice. The first revelation is that not only was Greece bankrupt in 2010 when the EU bailed it out, and that the bailout was designed to save the French and German banks, but that Angela Merkel and Nicolas Sarkozy knew this; and they knew it would be a disaster.
This charge is not new – it was levelled at the financial elite at the time by leftwing activists and rightwing economists. But Varoufakis substantiates it with quotes – some gleaned from the tapes of conversations and phone calls he was, unbeknown to the participants, making at the time. Even now, two years after the last Greek election, this is of more than academic interest. Greece remains burdened by billions of euros of debt it cannot pay. Because of the actions taken in 2010-11 – saving private banks by saddling north European states with massive debts – it is French and German taxpayers who will pay the price when the Greek debt is inevitably written off.

Not going to happen until after the German fall election.
• Greece, Creditors To Discuss Options For Debt Restructuring (CNBC)
Greece and its creditors are expected to discuss ways to restructure the country’s debt ahead of a meeting of euro zone finance ministers on May 22, a European official told CNBC on Tuesday. Athens agreed on Tuesday to introduce new laws on labor, energy reforms, pension cuts, and tax rises. This paves the way for a fresh disbursement of money from creditors in mid-June, but above all it allows Greece, its European creditors, and the IMF to consider how they will restructure the country’s debt. A European official who follows the bailout talks told CNBC that there isn’t a specific date for a solution to Greece’s debt but the first discussions on this issue will start soon. “From now until the Eurogroup meeting of May 22 there will be discussions to consider options for debt relief,” the official said.
Greece has to legislate the new reforms within two weeks. However, these new laws won’t take effect until 2019 and 2020 and will be dependent on the country’s economic performance. For example, among the new measures is the promise to cut pensions in 2019 and cut the tax-free threshold in 2020 to produce savings worth 2% of GDP. But if Athens exceeds its targets, it is allowed to offset the austerity measures and reduce taxes. During the first stages of talks on debt restructuring, the European Stability Mechanism, which is the euro zone’s permanent bailout fund, will produce a new debt sustainability analysis. Current economic forecasts indicate that Greece’s public debt stood at about 180% of GDP in 2016. The IMF will also be doing its debt sustainability analysis to include the recently-agreed measures.
The Fund wants an agreement on measures to make Greece’s debt more sustainable before deciding whether it is participating with its own money in the Greek bailout program. Dimitris Tzanakopoulos, spokesperson to the Greek government told reporters last month, that the IMF will make a “small” funding contribution that will not last for more than one year, so it ends at the same time as the current European program, which runs out in August of 2018. The IMF’s participation in the third bailout program to Greece is key for many euro countries, which perceive the fund’s involvement as giving credibility to the reform process in Greece. One of these countries is Germany, but the upcoming federal election might reduce Berlin’s room to restructure Greece’s debt.
“We will get some IMF participation, but no significant number,” Johannes Mayr, head of economic research at Bayern LB ,told CNBC via email. On the debt issue, “we need a compromise between the IMF and the EU/ESM (European Stability Mechanism), he said, “and this is realistic only after the German elections.” Neil Dwane, global strategist at Allianz Global Investors, added: “National governments, like Germany, would lose popularity if they wrote off Greek debt.” “I would expect more extend and pretend from the EU and the IMF,” he said via email.

No Greek default, but nothing else either: again, until after the German fall election. And even then.
• Greece Will Avoid Default After Bailout Deal – But Faces More Austerity (G.)
The long road to Greece emerging from its worst financial crisis in modern times reached another milestone on Tuesday as the country concluded a crucial compliance review that will allow it to avert default in July. At the cost of yet more painful austerity – in the form of extra pension cuts and tax increases – international creditors agreed to disburse €7.5bn (£6.3bn) in emergency loans to enable Athens to honour maturing debt repayments. More importantly, lenders accepted to set talks in motion on making Greece’s debt mountain more manageable – vital if the country is to gain access to the capital markets from which it has been almost completely exiled since 2009. [..] The deal ends more than six months of intense wrangling over the fiscal and structural reforms that Athens must implement in exchange for loans from its third, €86bn bailout programme.
Although the programme was outlined in 2015 when Greece came closest to crashing out of the eurozone and reverting to the drachma, the conditions attached to the lifeline remained open to negotiation. Discord most recently had focused on labour reforms and pensions – two issues that Tsakalotos, a British-trained Marxist economics professor, had felt especially strongly about. Under the agreement, the leftist-led government undertook to further slash pensions by 18% as of 2019. Pension payments have now been reduced 12 times since the start of the crisis, and cut by 40% in the past six years. With poorer out-of-work families often depending on them, news of a further drop was met with fury by union leaders, who immediately announced industrial action.
The two-party coalition led by the prime minister, Alexis Tsipras, also agreed to broaden the tax-free threshold by effectively dispensing with tax breaks as of 2020. Both measures are expected to produce savings worth €3.6bn or 2% of GDP. “It will be a very hot spring,” Odysseus Trivalas, acting president of the union of public sector employees, told the Guardian. “We have yet to see the details of this agreement but what we know is that it will mean further cuts. There will be a lot of strikes and a general 24-hour lockdown when the measures are brought to parliament for vote.”

“On a corner of Monastiraki Square full of tourists and passers-by, a group of volunteers from the soup kitchen O Allos Anthropos (The Fellow Man) cook chicken with rice. In less than 20 minutes, 230 hot meals are delivered to people who waited more than an hour to get them.”
• Greek Poverty Deepens During Seven Years Of Austerity (AP)
Over the past seven years, austerity has left visible scars in Greece’s capital. A walk around Athens reveals more homeless people than ever despite some signs of a rosier economic outlook. Thousands of shops, mostly small businesses, are shuttered here and across the country. In what used to be a busy shopping arcade, closed stores are padlocked against a backdrop of hanging Greek flags. Whole families can be seen lining up for free meals at a growing number of soup kitchens. “Every day we feed 400 to 500 people, and this number has increased even more in the past two years,” says Evangelia Konsta, organizer and sponsor of the meals offered by the Church of Greece in a run-down neighborhood in central Athens.
Yesterday, IMF and European negotiators bailout negotiators reached an agreement with Greece’s government to continue rescue funding in return for a painful new round of cuts and higher taxes over the next three years. High unemployment and a steady decline of living standards for most Greeks for seven consecutive years have had lasting effects. Greece has survived on international rescue loans since 2010, granted by the IMF and other countries using the euro currency in exchange for drastic cuts in public spending and benefits. Greece is now in its third bailout. A few steps away from the Church-run soup kitchen is a homeless shelter also run by the Church. Guests in its tiny rooms include one family with their young children and a retired nurse suffering from cancer who is still waiting to get her pension application approved.
Another shelter, the “Shelter of Love and Solidarity,” has a great view of the ancient Acropolis that’s barely noticed by the hundreds of homeless and poor who come twice a week to wash their clothes and take a hot bath. “The shelter is the best option for us because the government doesn’t really do anything for us,” says Ilias Kosmidis, 38, who has been sleeping on the street for the past two years. While waiting to wash their clothes, people at the shelter have developed friendships, and catch up on the news, including the French presidential election. Sofia Vitalaki and her husband Costas, both retired civil servants, have run the shelter since 1991. “It’s not just the food,” she says. “Most people want their dignity back and here we try to support them.”
On a corner of Monastiraki Square full of tourists and passers-by, a group of volunteers from the soup kitchen O Allos Anthropos (The Fellow Man) cook chicken with rice. In less than 20 minutes, 230 hot meals are delivered to people who waited more than an hour to get them. At the end of every month, it’s become a familiar sight outside banks: pensioners waiting in huge lines to collect their monthly checks. Few know how to use ATMs. While in line, they fret over how to make ends meet after years of cuts to their earnings, worrying about more austerity being planned. They won’t have long to wait till the next round of cuts. The government on Tuesday finalized its agreement with bailout lenders to ax pensions further, starting on January 1, 2019.