
Paul Klee Ghost of a Genius 1922
The Automatic Earth has written many articles on the topic of EROEI (Energy Return on Energy Invested) through the years, there’s a whole chapter on it in the Automatic Earth Primer Guide 2017 that Nicole assembled recently, which contains 17 different articles.
Still, since EROEI is the most important energy issue there is at present, and not the price of oil or some new gas find or a set of windmills or solar panels or thorium, it can’t hurt to repeat it once again, in someone else’s words and from someone else’s angle. This one comes from Brian Davey on his site CredoEconomics, part of his book “Credo”.
It can’t hurt to repeat it because not nearly enough people understand that in the end everything, the survival of our world, our way of life, is all about the ‘quality’ of energy, about what we get in return when we drill and pump and build infrastructure, what remains when we subtract all the energy used to ‘generate’ energy, from (or at) the bottom line.
Anno 2017, our overall ‘net energy’ is nowhere near where it was for the first 100 years or so after we started using oil. And there’s no energy source that comes close to -conventional- oil (and gas) when it comes to what we are left with once our efforts are discounted, in calories or Joules.
The upshot of this is that even if we can ‘gain’ 10 times more than we put in, in energy terms, that won’t save our complex societies. To achieve that, we would need at least a 15:1 ratio, a number straight from our friend Charlie Hall, which is probably still quite optimistic. And we simply don’t have it. Not anymore.
Also, not nearly enough people understand that it has absolutely nothing to do with money. That you can’t go out and buy more or better energy sources. Which is why we use EROEI instead of EROI (Energy Return on Investment), because the latter leaves some sort of financial interpretation open that doesn’t actually exist, it suggests that a financial price of energy plays a role.
First, here’s Nicole from the Automatic Earth Primer Guide 2017. Below that, Brian Davey’s article.

Nicole Foss: Energy is the master resource – the capacity to do work. Our modern society is the result of the enormous energy subsidy we have enjoyed in the form of fossil fuels, specifically fossil fuels with a very high energy profit ratio (EROEI). Energy surplus drove expansion, intensification, and the development of socioeconomic complexity, but now we stand on the edge of the net energy cliff. The surplus energy, beyond that which has to be reinvested in future energy production, is rapidly diminishing.
We would have to greatly increase gross production to make up for reduced energy profit ratio, but production is flat to falling so this is no longer an option. As both gross production and the energy profit ratio fall, the net energy available for all society’s other purposes will fall even more quickly than gross production declines would suggest. Every society rests on a minimum energy profit ratio. The implication of falling below that minimum for industrial society, as we are now poised to do, is that society will be forced to simplify.
A plethora of energy fantasies is making the rounds at the moment. Whether based on unconventional oil and gas or renewables (that are not actually renewable), these are stories we tell ourselves in order to deny that we are facing any kind of future energy scarcity, or that supply could be in any way a concern. They are an attempt to maintain the fiction that our society can continue in its current form, or even increase in complexity. This is a vain attempt to deny the existence of non-negotiable limits to growth. The touted alternatives are not energy sources for our current society, because low EROEI energy sources cannot sustain a society complex enough to produce them.

Using Energy to Extract Energy – The Dynamics of Depletion
Brian Davey: The “Limits to Growth Study” of 1972 was deeply controversial and criticised by many economists. Over 40 years later, it seems remarkably prophetic and on track in its predictions. The crucial concept of Energy Return on Energy Invested is explained and the flaws in neoclassical reasoning which EROI highlights.
The continued functioning of the energy system is a “hub interdependency” that has become essential to the management of the increasing complexity of our society. The energy input into the UK economy is about 50 to 70 times as great as what the labour force could generate if working full time only with the power of their muscles, fuelled up with food. It is fossil fuels, refined to be used in vehicles and motors or converted into electricity that have created power inputs that makes possible the multiple round- about arrangements in a high complex economy. The other “hub interdependency” is a money and transaction system for exchange which has to continue to function to make vast production and trade networks viable. Without payment systems nothing functions.
Yet, as I will show, both types of hub interdependencies could conceivably fail. The smooth running of the energy system is dependent on ample supplies of cheaply available fossil fuels. However, there has been a rising cost of extracting and refining oil, gas and coal. Quite soon there is likely to be an absolute decline in their availability. To this should be added the climatic consequences of burning more carbon based fuels. To make the situation even worse, if the economy gets into difficulty because of rising energy costs then so too will the financial system – which can then have a knock-on consequence for the money system. The two hub interdependencies could break down together.
“Solutions” put forward by the techno optimists almost always assume growing complexity and new uses for energy with an increased energy cost. But this begs the question- because the problem is the growing cost of energy and its polluting and climate changing consequences.
The “Limits to Growth” study of 1972 – and its 40 year after evaluation
It was a view similar to this that underpinned the methodology of a famous study from the early 1970s. A group called the Club of Rome decided to commission a group of system scientists at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology to explore how far economic growth would continue to be possible. Their research used a series of computer model runs based on various scenarios of the future. It was published in 1972 and produced an instant storm. Most economists were up in arms that their shibboleth, economic growth, had been challenged. (Meadows, Meadows, Randers, & BehrensIII, 1972)
This was because its message was that growth could continue for some time by running down “natural capital” (depletion) and degrading “ecological system services” (pollution) but that it could not go on forever. An analogy would be spending more than one earns. This is possible as long as one has savings to run down, or by running up debts payable in the future. However, a day of reckoning inevitably occurs. The MIT scientists ran a number of computer generated scenarios of the future including a “business as usual” projection, called the “standard run” which hit a global crisis in 2030.
It is now over 40 years since the original Limits to Growth study was published so it is legitimate to compare what was predicted in 1972 against what actually happened. This has now been done twice by Graham Turner who works at the Australian Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO). Turner did this with data for the rst 30 years and then for 40 years of data. His conclusion is as follows:
The Limits to Growth standard run scenario produced 40 years ago continues to align well with historical data that has been updated in this paper following a 30-year comparison by the author. The scenario results in collapse of the global economy and environment and subsequently, the population. Although the modelled fall in population occurs after about 2030 – with death rates reversing contemporary trends and rising from 2020 onward – the general onset of collapse first appears at about 2015 when per capita industrial output begins a sharp decline. (Turner, 2012)
So what brings about the collapse? In the Limits to Growth model there are essentially two kinds of limiting restraints. On the one hand, limitations on resource inputs (materials and energy). On the other hand, waste/pollution restraints which degrade the ecological system and human society (particularly climate change).
Turner finds that, so far it, is the former rather than the latter that is the more important. What happens is that, as resources like fossil fuels deplete, they become more expensive to extract. More industrial output has to be set aside for the extraction process and less industrial output is available for other purposes.
With signficant capital subsequently going into resource extraction, there is insufficient available to fully replace degrading capital within the industrial sector itself. Consequently, despite heightened industrial activity attempting to satisfy multiple demands from all sectors and the population, actual industrial output per capita begins to fall precipitously, from about 2015, while pollution from the industrial activity continues to grow. The reduction of inputs produced per capita. Similarly, services (e.g., health and education) are not maintained due to insufficient capital and inputs.
Diminishing per capita supply of services and food cause a rise in the death rate from about 2020 (and somewhat lower rise in the birth rate, due to reduced birth control options). The global population therefore falls, at about half a billion per decade, starting at about 2030. Following the collapse, the output of the World3 model for the standard run (figure 1 to figure 3) shows that average living standards for the aggregate population (material wealth, food and services per capita) resemble those of the early 20th century.(Turner, 2012, p. 121)
Energy Return on Energy Invested
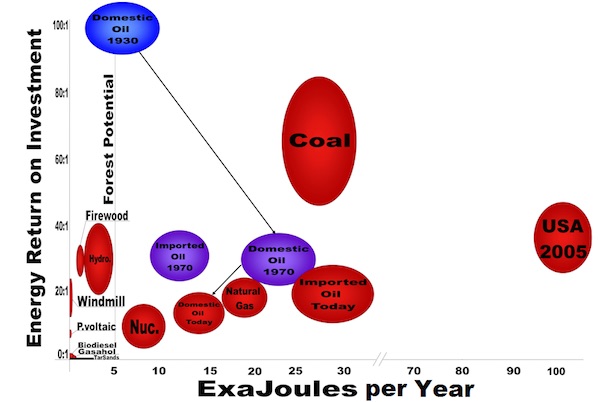
A similar analysis has been made by Hall and Klitgaard. They argue that to run a modern society it is necessary that the energy return on energy invested must be at least 15 to 1. To understand why this should be so consider the following diagram from a lecture by Hall. (Hall, 2012)

The diagram illustrates the idea of the energy return on energy invested. For every 100 Mega Joules of energy tapped in an oil flow from a well, 10 MJ are needed to tap the well, leaving 90 MJ. A narrow measure of energy returned on energy invested at the wellhead in this example would therefore be 100 to 10 or 10 to 1.
However, to get a fuller picture we have to extend this kind of analysis. Of the net energy at the wellhead, 90 MJ, some energy has to be used to refine the oil and produce the by-products, leaving only 63 MJ.
Then, to transport the refined product to its point of use takes another 5 MJ leaving 58MJ. But of course, the infrastructure of roads and transport also requires energy for construction and maintenance before any of the refined oil can be used to power a vehicle to go from A to B. By this final stage there is only 20.5 MJ of the original 100MJ left.
We now have to take into account that depletion means that, at well heads around the world, the energy to produce energy is increasing. It takes energy to prospect for oil and gas and if the wells are smaller and more difficult to tap because, for example, they are out at sea under a huge amount of rock. Then it will take more energy to get the oil out in the first place.
So, instead of requiring 10MJ to produce the 100 MJ, let us imagine that it now takes 20 MJ. At the other end of the chain there would thus, only be 10.5MJ – a dramatic reduction in petroleum available to society.
The concept of Energy Return on Energy Invested is a ratio in physical quantities and it helps us to understand the flaw in neoclassical economic reasoning that draws on the idea of “the invisible hand” and the price mechanism. In simplistic economic thinking, markets should have no problems coping with depletion because a depleting resource will become more expensive. As its price rises, so the argument goes, the search for new sources of energy and substitutes will be incentivised while people and companies will adapt their purchases to rising prices. For example, if it is the price of energy that is rising then this will incentivise greater energy efficiency. Basta! Problem solved…
Except the problem is not solved… there are two flaws in the reasoning. Firstly, if the price of energy rises then so too does the cost of extracting energy – because energy is needed to extract energy. There will be gas and oil wells in favourable locations which are relatively cheap to tap, and the rising energy price will mean that the companies that own these wells will make a lot of money. This is what economists call “rent”. However, there will be some wells that are “marginal” because the underlying geology and location are not so favourable. If energy prices rise at these locations then rising energy prices will also put up the energy costs of production. Indeed, when the energy returned on energy invested falls as low as 1 to 1, the increase in the costs of energy inputs will cancel out any gains in revenues from higher priced energy outputs. As is clear when the EROI is less than one, energy extraction will not be profitable at any price.
Secondly, energy prices cannot in any case rise beyond a certain point without crashing the economy. The market for energy is not like the market for cans of baked beans. Energy is necessary for virtually every activity in the economy, for all production and all services. The price of energy is a big deal – energy prices going up and down have a similar significance to interest rates going up or down. There are “macro-economic” consequences for the level of activity in the economy. Thus, in the words of one analyst, Chris Skrebowski, there is a rise in the price of oil, gas and coal at which:
the cost of incremental supply exceeds the price economies can pay without destroying growth at a given point in time.(Skrebowski, 2011)
This kind of analysis has been further developed by Steven Kopits of the Douglas-Westwood consultancy. In a lecture to the Columbia University Center on Global Energy Policy in February of 2014, he explained how conventional “legacy” oil production peaked in 2005 and has not increased since. All the increase in oil production since that date has been from unconventional sources like the Alberta Tar sands, from shale oil or natural gas liquids that are a by-product of shale gas production. This is despite a massive increase in investment by the oil industry that has not yielded any increase in “conventional oil” production but has merely served to slow what would otherwise have been a faster decline.
More specifically, the total spend on upstream oil and gas exploration and production from 2005 to 2013 was $4 trillion. Of that amount, $3.5 trillion was spent on the “legacy” oil and gas system. This is a sum of money equal to the GDP of Germany. Despite all that investment in conventional oil production, it fell by 1 million barrels a day. By way of comparison, investment of $1.5 trillion between 1998 and 2005 yielded an increase in oil production of 8.6 million barrels a day.
Further to this, unfortunately for the oil industry, it has not been possible for oil prices to rise high enough to cover the increasing capital expenditure and operating costs. This is because high oil prices lead to recessionary conditions and slow or no growth in the economy. Because prices are not rising fast enough and costs are increasing, the costs of the independent oil majors are rising at 2 to 3% a year more than their revenues. Overall profitability is falling and some oil majors have had to borrow and sell assets to pay dividends. The next stage in this crisis has then been that investment projects are being cancelled – which suggests that oil production will soon begin to fall more rapidly.
The situation can be understood by reference to the nursery story of Goldilocks and the Three Bears. Goldilocks tries three kinds of porridge – some that is too hot, some that is too cold and some where the temperature is somewhere in the middle and therefore just right. The working assumption of mainstream economists is that there is an oil price that is not too high to undermine economic growth but also not too low so that the oil companies cannot cover their extraction costs – a price that is just right. The problem is that the Goldilocks situation no longer describes what is happening. Another story provides a better metaphor – that story is “Catch 22”. According to Kopits, the vast majority of the publically quoted oil majors require oil prices of over $100 a barrel to achieve positive cash flow and nearly a half need more than $120 a barrel.
But it is these oil prices that drag down the economies of the OECD economies. For several years, however, there have been some countries that have been able to afford the higher prices. The countries that have coped with the high energy prices best are the so called “emerging non OECD countries” and above all China. China has been bidding away an increasing part of the oil production and continuing to grow while higher energy prices have led to stagnation in the OECD economies. (Kopits, 2014)
Since the oil price is never “just right” it follows that it must oscillate between a price that is too high for macro-economic stability or too low to make it a paying proposition for high cost producers of oil (or gas) to invest in expanding production. In late 2014 we can see this drama at work. The faltering global economy has a lower demand for oil but OPEC, under the leadership of Saudi Arabia, have decided not to reduce oil production in order to keep oil prices from falling. On the contrary they want prices to fall. This is because they want to drive US shale oil and gas producers out of business.
The shale industry is described elsewhere in this book – suffice it here to refer to the claim of many commentators that the shale oil and gas boom in the United States is a bubble. A lot of money borrowed from Wall Street has been invested in the industry in anticipation of high profits but given the speed at which wells deplete it is doubtful whether many of the companies will be able to cover their debts. What has been possible so far has been largely because quantitative easing means capital for this industry has been made available with very low interest rates. There is a range of extraction production costs for different oil and gas wells and fields depending on the differing geology in different places. In some “sweet spots” the yield compared to cost is high but in a large number of cases the costs of production have been high and it is being said that it will be impossible to make money at the price to which oil has fallen ($65 in late 2014). This in turn could mean that companies funding their operations with junk bonds could find it difficult to service their debt. If interest rates rise the difficulty would become greater. Because the shale oil and gas sector has been so crucial to expansion in the USA then a large number of bankruptcies could have wider repercussions throughout the wider US and world economy.
Renewable Energy systems to the rescue?
Although it seems obvious that the depletion of fossil fuels can and should lead to the expansion of renewable energy systems like wind and solar power, we should beware of believing that renewable energy systems are a panacea that can rescue consumer society and its continued growth path. A very similar net energy analysis can, and ought to be done for the potential of renewable energy to match that already done for fossil fuels.
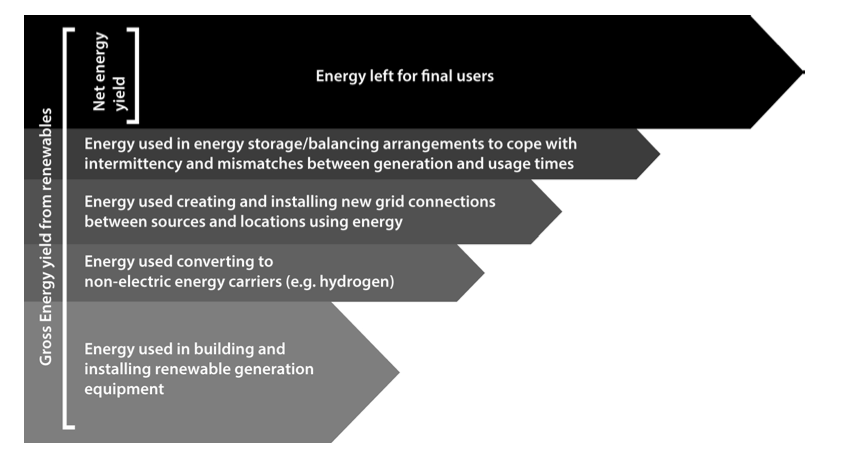
Before we get over-enthusiastic about the potential for renewable energy, we have to be aware of the need to subtract the energy costs particular to renewable energy systems from the gross energy that renewable energy systems generate. Not only must energy be used to manufacture and install the wind turbines, the solar panels and so on, but for a renewable based economy to be able to function, it must also devote energy to the creation of energy storage. This would allow for the fact that, when the wind and the sun are generating energy, is not necessarily the time when it is wanted.
Furthermore, the places where, for example, solar and wind potential are at this best – offshore for wind or in deserts without dust storms near the equator for solar – are usually a long distance from centres of use. Once again, a great deal of energy, materials and money must be spent getting the energy from where it is generated to where it will be used. For example, the “Energie Wende” (Energy Transformation) in Germany is involving huge effort, financial and energy costs, creating a transmission corridor to carry electricity from North Sea wind turbines down to Bavaria where the demand is greatest. Similarly, plans to develop concentrated solar power in North Africa for use in northern Europe which, if they ever come to anything, will require major investments in energy transmission. A further issue, connected to the requirement for energy storage, is the need for energy carriers which are not based on electricity. As before, conversions to put a current energy flux into a stored form, involve an energy cost.
Just as with fossil fuels, sources of renewable energy are of variable yield depending on local conditions: offshore wind is better than onshore for wind speed and wind reliability; there is more solar energy nearer the equator; some areas have less cloud cover; wave energy on the Atlantic coasts of the UK are much better than on other coastlines like those of the Irish Sea or North Sea. If we make a Ricardian assumption that best net yielding resources are developed first, then subsequent yields will be progressively inferior. In more conventional jargon – just as there are diminishing returns for fossil energy as fossil energy resources deplete, so there will eventually be diminishing returns for renewable energy systems. No doubt new technologies will partly buck this trend but the trend is there nonetheless. It is for reasons such as these that some energy experts are sceptical about the global potential of renewable energy to meet the energy demand of a growing economy. For example, two Australian academics at Monash University argue that world energy demand would grow to 1,000 EJ (EJ = 10 18 J) or more by 2050 if growth continued on the course of recent decades. Their analysis then looks at each renewable energy resource in turn, bearing in mind the energy costs of developing wind, solar, hydropower, biomass etc., taking into account diminishing returns, and bearing in mind too that climate change may limit the potential of renewable energy. (For example, river flow rates may change affecting hydropower). Their conclusion: “We nd that when the energy costs of energy are considered, it is unlikely that renewable energy can provide anywhere near a 1000 EJ by 2050.” (Moriarty & Honnery, 2012)
Now let’s put these insights back into a bigger picture of the future of the economy. In a presentation to the All Party Parliamentary Group on Peak Oil and Gas, Charles Hall showed a number of diagrams to express the consequences of depletion and rising energy costs of energy. I have taken just two of these diagrams here – comparing 1970 with what might be the case in 2030. (Hall C. , 2012) What they show is how the economy produces different sorts of stuff. Some of the production is consumer goods, either staples (essentials) or discretionary (luxury) goods. The rest of production is devoted to goods that are used in production i.e. investment goods in the form of machinery, equipment, buildings, roads, infrastracture and their maintenance. Some of these investment goods must take the form of energy acquisition equipment. As a society runs up against energy depletion and other problems, more and more production must go into energy acquisition, infrastructure and maintenance. Less and less is available for consumption, and particularly for discretionary consumption.
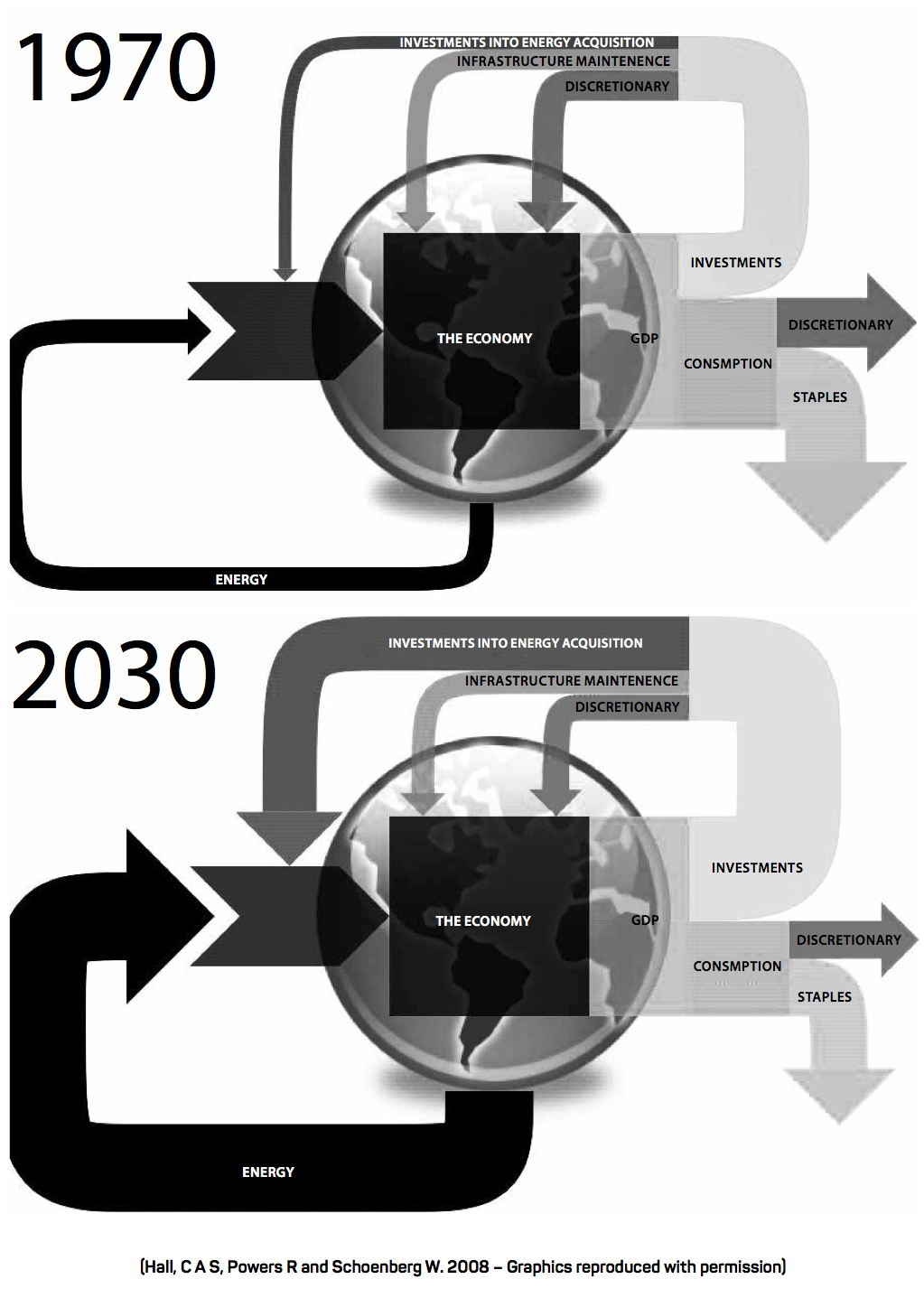
Whether the economy would evolve in this way can be questioned. As we have seen, the increasing needs of the oil and gas sector implies a transfer of resources from elsewhere through rising prices. However, the rest of the economy cannot actually pay this extra without crashing. That is what the above diagrams show – a transfer of resources from discretionary consumption to investment in energy infrastructure. But such a transfer would be crushing for the other sectors and their decline would likely drag down the whole economy.
Over the last few years, central banks have had a policy of quantitative easing to try to keep interest rates low. The economy cannot pay high energy prices AND high interest rates so, in effect, the policy has been to try to bring down interest rates as low as possible to counter the stagnation. However, this has not really created production growth, it has instead created a succession of asset price bubbles. The underlying trend continues to be one of stagnation, decline and crisis and it will get a lot worse when oil production starts to fall more rapidly as a result of investment cut backs. The severity of the recessions may be variable in different countries because competitive strength in this model goes to those countries where energy is used most efficiently and which can afford to pay somewhat higher prices for energy. Such countries are likely to do better but will not escape the general decline if they stay wedded to the conventional growth model. Whatever the variability, this is still a dead end and, at some point, people will see that entirely different ways of thinking about economy and ecology are needed – unless they get drawn into conflicts and wars over energy by psychopathic policy idiots. There is no way out of the Catch 22 within the growth economy model. That’s why degrowth is needed.
Further ideas can be extrapolated from Hall’s way of presenting the end of the road for the growth economy. The only real option as a source for extra resources to be ploughed into changing the energy sector is from what Hall calls “discretionary consumption” aka luxury consumption. It would not be possible to take from “staples” without undermining the ability of ordinary people to survive day to day. Implicit here is a social justice agenda for the post growth – post carbon economy. Transferring resources out of the luxury consumption of the rich is a necessary part of the process of finding the wherewithal for energy conservation work and for developing renewable energy resources. These will be expensive and the resources cannot come from anywhere else than out of the consumption of the rich. It should be remembered too that the problems of depletion do not just apply to fossil energy extraction coal, oil and gas) but apply across all forms of mineral extraction. All minerals are depleted by use and that means the grade or ore declines over time. Projecting the consequences into the future ought to frighten the growth enthusiasts. To take in how industrial production can hit a brick wall of steeply rising costs, consider the following graph which shows the declining quality of ore grades mined in Australia.

As ores deplete there is a deterioration of ore grades. That means that more rock has to be shifted and processed to refine and extract the desired raw material, requiring more energy and leaving more wastes. This is occurring in parallel to the depletion in energy sources which means that more energy has to be used to extract a given quantity of energy and therefore, in turn, to extract from a given quantity of ore. Thus, the energy requirements to extract energy are rising at the very same time as the amount of energy required to extract given quantities of minerals are rising. More energy is needed just at the time that energy is itself becoming more expensive.
Now, on top of that, add to the picture the growing demand for minerals and materials if the economy is to grow.
At least there has been a recognition and acknowledgement in recent years that environmental problems exist. The problem is now somewhat different – the problem is the incredibly naive faith that markets and technology can solve all problems and keep on going. The main criticism of the limits to growth study was the claim that problems would be anticipated in forward markets and would then be made the subject of high tech innovation. In the next chapter, the destructive effects of these innovations are examined in more depth.
















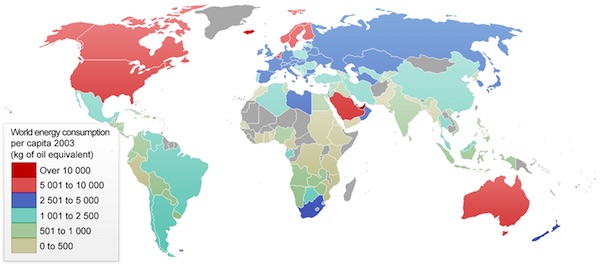
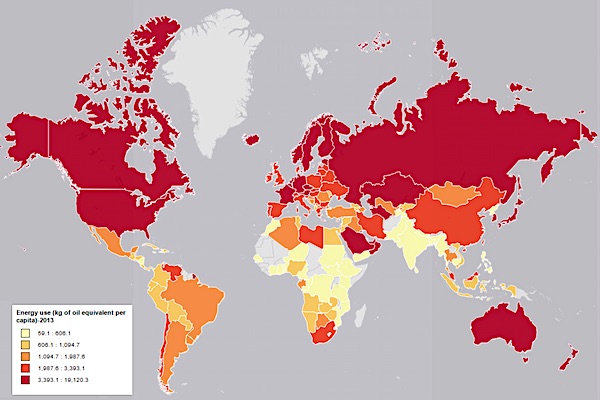






 This question generated a number of comments in the last Blowout so I thought I would take a quick look at it. I find that the electrified portion of the Dutch railway network (Nederlandse Spoorwegen, or NS) runs on grid electricity that comes dominantly from fossil fuel generation (natural gas and coal). NS claims 100% wind power because it has a contract with various wind farms to produce enough energy to power its rail system, but this is just an accounting transaction. Only a small fraction of the power delivered to its trains actually comes from wind.
This question generated a number of comments in the last Blowout so I thought I would take a quick look at it. I find that the electrified portion of the Dutch railway network (Nederlandse Spoorwegen, or NS) runs on grid electricity that comes dominantly from fossil fuel generation (natural gas and coal). NS claims 100% wind power because it has a contract with various wind farms to produce enough energy to power its rail system, but this is just an accounting transaction. Only a small fraction of the power delivered to its trains actually comes from wind.









