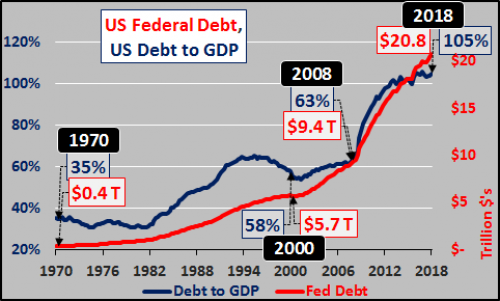
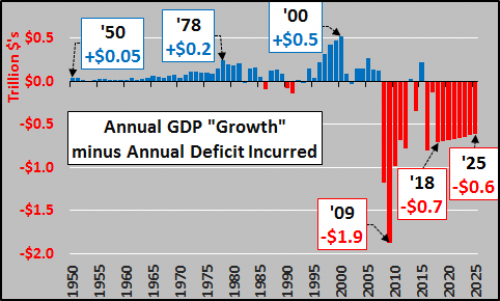
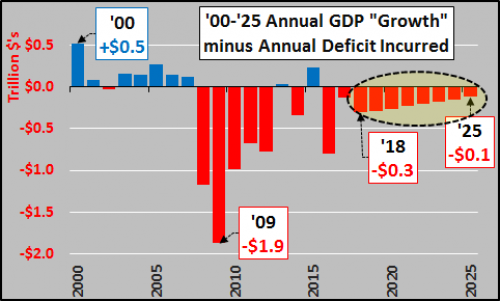
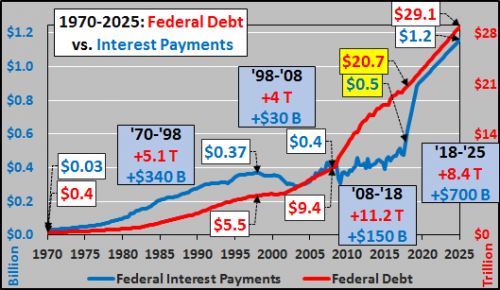
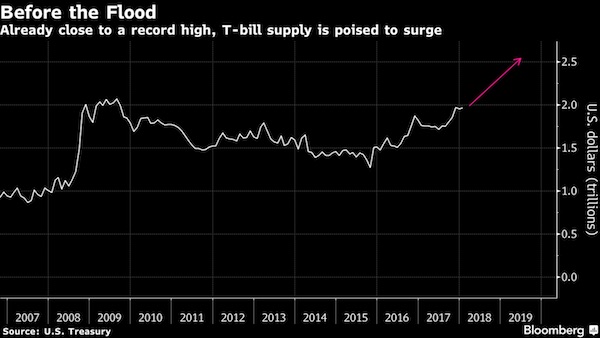
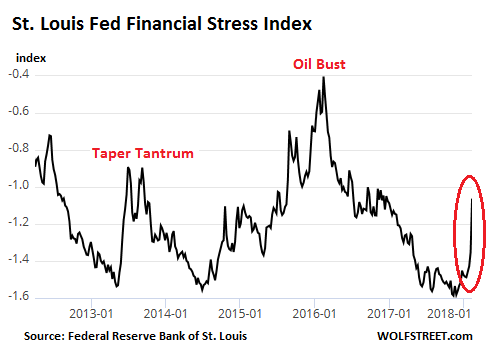
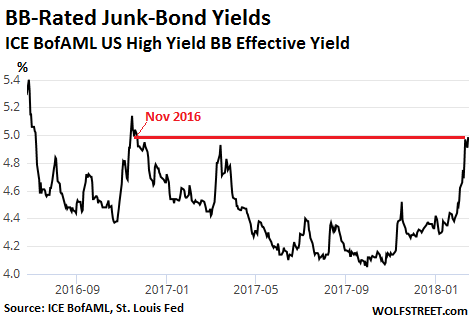
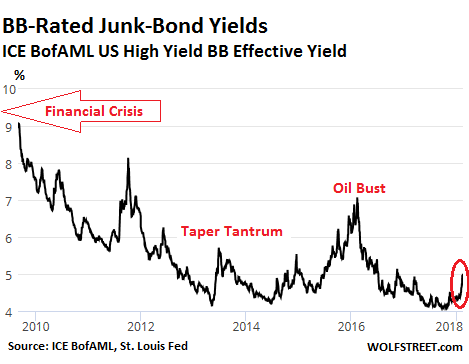
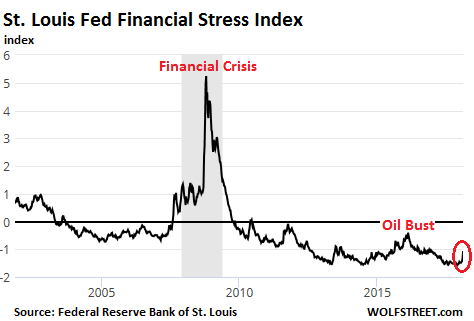
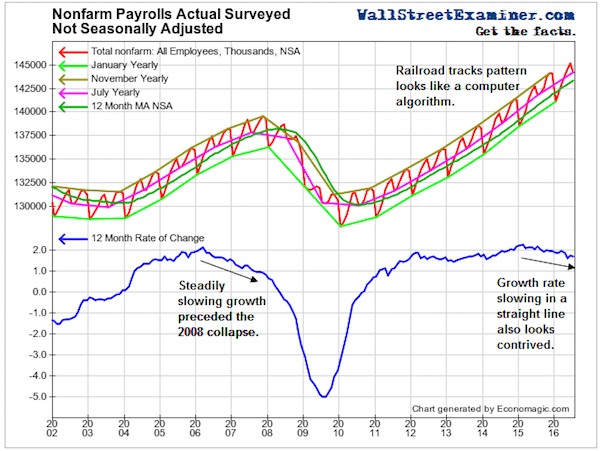
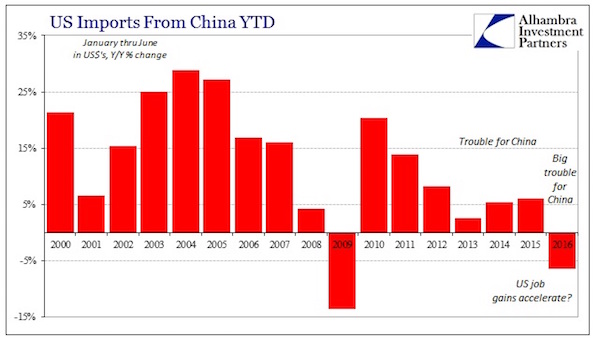
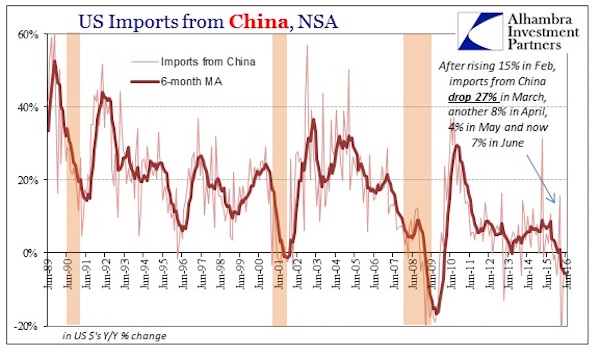
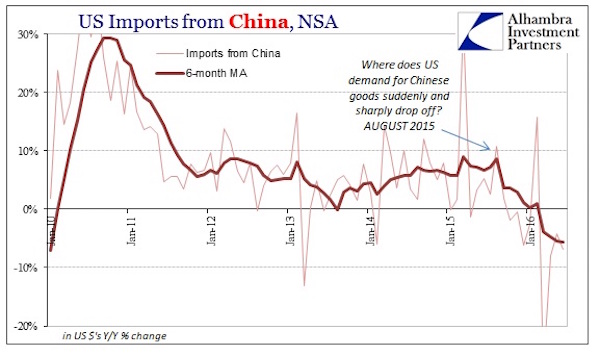
John French Sloan A Woman’s Work 1912

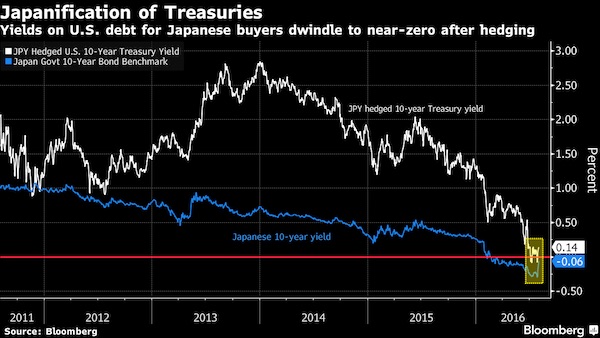
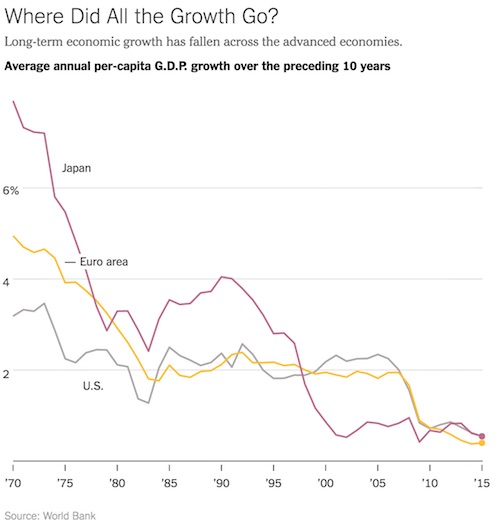
Abenomics is a miserable failure. Which is why Abe’s popularity is scraping the gutter. But we keep on pretending. Five years? Why not make it ten, or fifty? Kuroda is stuck….
• Japan Can Begin Reducing Stimulus In Five Years – Kuroda (CNBC)
The Bank of Japan will be able to begin winding down its extraordinary monetary stimulus within the next five years, the head of the central bank said. “Sometime within the next five years, we will reach [our] 2% inflation target,” Governor Haruhiko Kuroda told CNBC’s Sara Eisen over the weekend. Once that level is reached, we will start “discussing how to gradually normalize the monetary condition.” Kuroda began his second five-year term this year. He has implemented a massive stimulus policy by cutting the central bank’s benchmark interest rate to negative, keeping the 10-year Japanese government bond yield near 0% in an effort to control the yield curve and stepping up the Bank of Japan’s asset purchases.
However, inflation remains low. Japan reported its consumer price index, excluding fresh food and energy, rose 0.5% in the 12 months through March. “In order to reach [our] 2% inflation target, I think the Bank of Japan must continue very strong accommodative monetary policy for some time,” Kuroda added in his interview with CNBC. Japan’s efforts to boost the sluggish national economy come amid steady growth around the world. The IMF predicts the global economy will increase 3.9% this year and next. Kuroda agreed with the positive outlook. “The world economy will continue to grow at a relatively high pace,” he said. For this year and next, “we don’t see any sign of a turning point.” But protectionism, unexpected rapid tightening of monetary policy in some countries, and geopolitical tensions in North Korea and the Middle East pose potential risks, Kuroda said.
Read more …

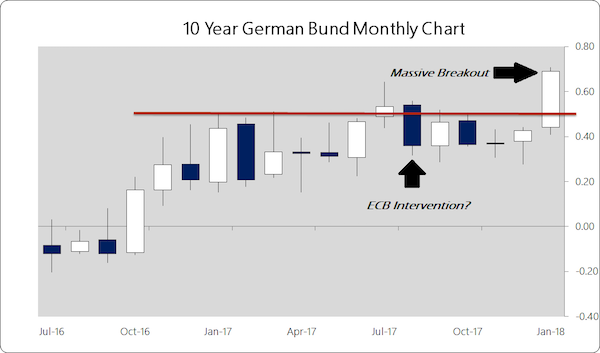
… and Draghi is stuck too. My article yesterday was timely. The outgoing Bundesbank director in charge of banking supervision says the ECB’s credibility is at stake. A dangerous thing to say.
• ECB Mulls Shelving Rules Tackling Euro Zone’s Bad Loans Pile (R.)
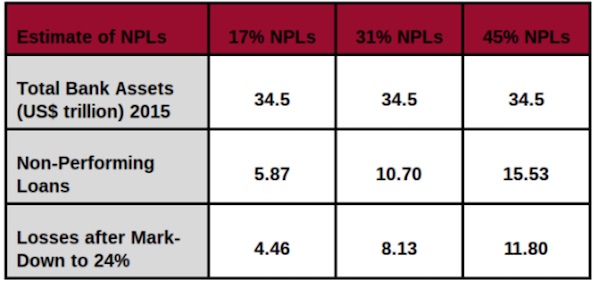
The European Central Bank, after suffering a political backlash, is considering shelving planned rules that would have forced banks to set aside more money against their stock of unpaid loans. The guidelines, which were expected by March, had been presented as a main plank of the ECB’s plan to bring down a 759 billion euro ($930 billion) pile of soured credit weighing on euro zone banks, particularly in Greece, Portugal and Italy. The ECB was now considering whether further policies on legacy non-performing loans (NPLs) were necessary “depending on the progress made by individual banks”, an ECB spokeswoman said.
No decision had been made yet and the next steps were still being evaluated, she said. Central Bank sources told Reuters that if the rules were scrapped, supervisors would look to continue putting pressure on problem banks using existing powers. An alternative would be to hold off until the results of pan-European stress tests are published in November but this would be close to the end of Daniele Nouy’s mandate as the head of the ECB’s Single Supervisory Mechanism at the end of the year. A clean-up of banks’ balance sheets from toxic assets inherited from the financial crisis is a precondition for getting countries like Germany to agree on a common euro zone insurance on bank deposits.
And Andreas Dombret, the outgoing Bundesbank director in charge of banking supervision, said in an interview published on Monday that the ECB’s credibility was at stake. “One cannot say that NPLs are one of the biggest risk for the European banking sector and a top priority and then fail to act,” he told Boersen-Zeitung. “It’s about the credibility of the SSM,” he said, calling for a “timely proposal”.
Read more …

And as the central bankers find themselves trapped, the bond vigilantes roam free.
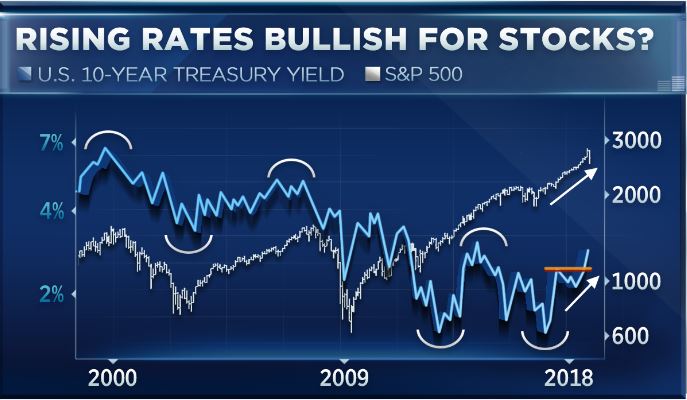
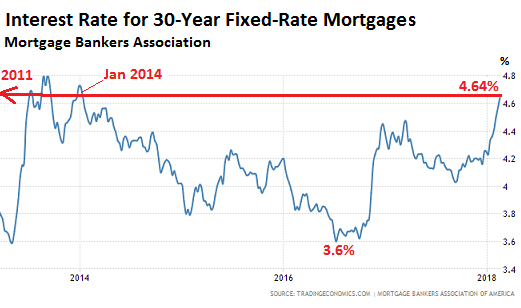
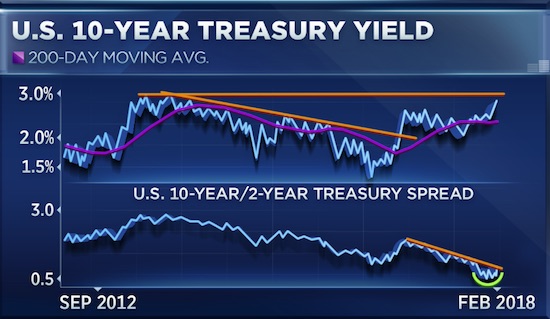
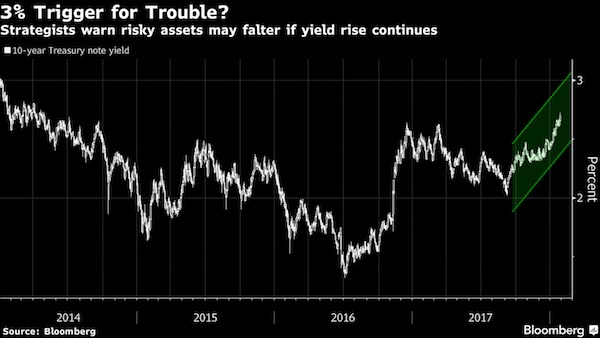
• The Return Of Honest Bond Yields (Stockman)
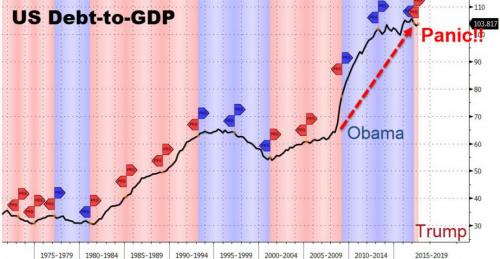
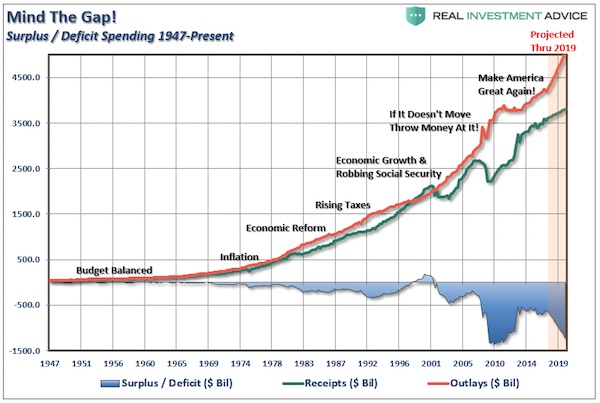
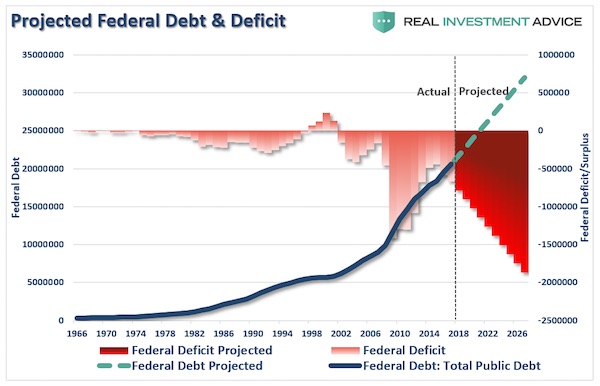
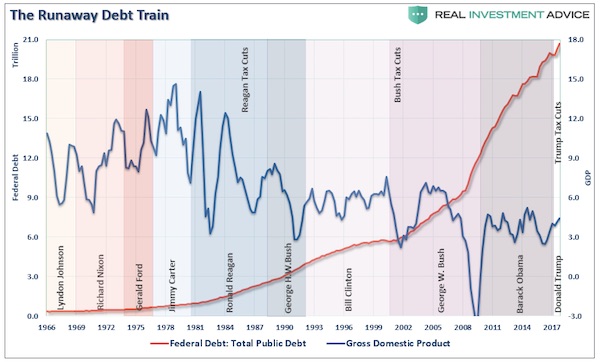
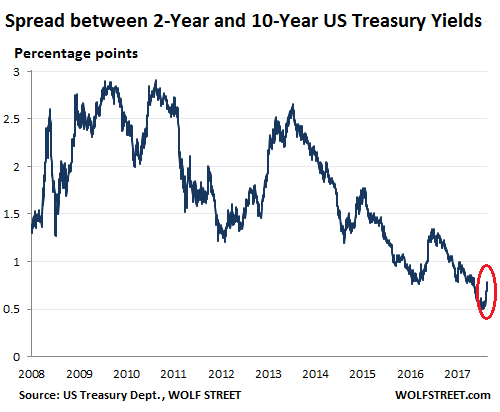
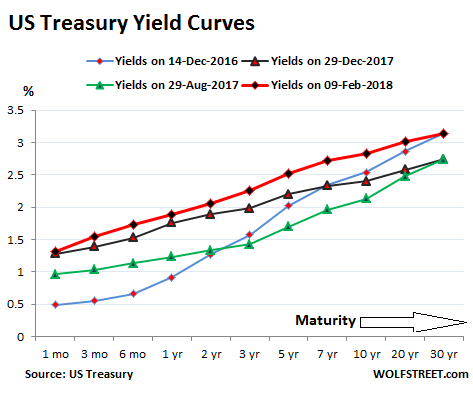
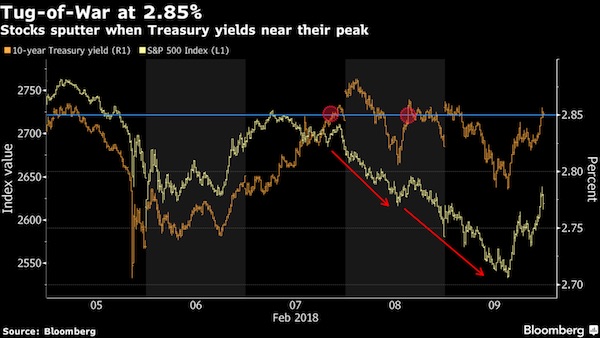
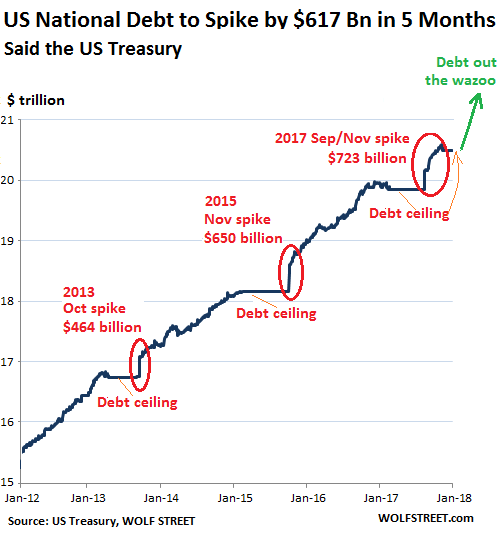
In the wee hours this AM, the yield on the 10-year treasury note hit 2.993%. That’s close enough for gubermint work to say that the big 3.00% inflection point has now been tripped. And it means, in turn, that the end days of the Bubble Finance era have well and truly commenced. In a word, honest bond yields will knock the stuffings out of the mainstream fairy tale that passes for economic and financial reality. And in a 2-3% inflation world, by honest bond yields we mean 3% + on the front-end and 4-5% on the back-end of the yield curve. Needless to say, that means big trouble for the myth of MAGA. As we demonstrated in part 2, since the Donald’s inauguration there has been no acceleration in the main street economy—just the rigor mortis spasms of a stock market that has been endlessly juiced with cheap debt.
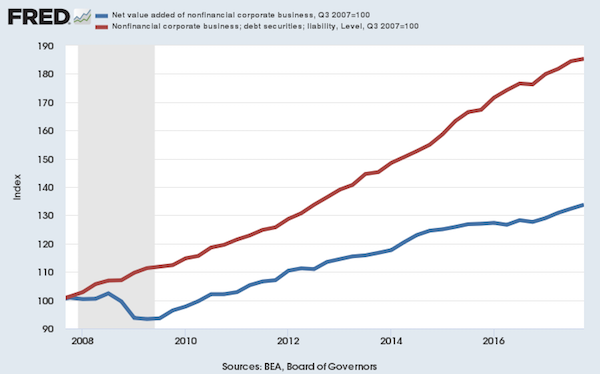
But the Trump boomlet in the stock averages has now hit its sell-by date. That’s because today’s egregiously inflated equity prices are in large part a product of debt-fueled corporate financial engineering—stock buybacks, unearned dividends and massive M&A dealing. Thus, since the pre-crisis peak in Q3 2007 nonfinancial corporate sector value added is up by 34%, but corporate debt securities outstanding have risen by 85%; and the overwhelming share of that massive debt increase was used to fund financial engineering, not productive assets and future earnings growth. In a world of honest interest rates, of course, this explosion of non-productive debt would have chewed into earnings good and hard because the borrowed cash went to Wall Street, not into the wherewithal of earnings growth.
In fact, during the past 10 years, net value added generated by US nonfinancial corporations rose by just $2 trillion (from $6.1 trillion to $8.1 trillion per annum), whereas corporate debt rose by nearly $3 trillion (from $3.3 trillion to $6.1 trillion). So it should have been a losing battle—with interest expense rising far faster than operating profits. But owing to the Fed’s misguided theory that it can make the main street economy bigger and stronger by falsifying interest rates and other financial asset prices, the C-suite financial engineers got a free hall pass. That is, they pleasured Wall Street by pumping massive amounts of borrowed cash back into the casino, but got no black mark on their P&Ls.
Read more …

“That’s what happens when money is just a representation of debt that can’t be paid back.”
• Stop and Assess (Jim Kunstler)
Let’s pause today and make an assessment of where things stand in this country as Winter finally coils into Spring. As you might expect, a nation overrun with lawyers has litigated itself into a cul-de-sac of charges, arrests, suits, countersuits, and allegations that will rack up billable hours until the Rockies tumble. The best outcome may be that half the lawyers in this land will put the other half in jail, and then, finally, there will be space for the rest of us to re-connect with reality.
What does that reality consist of? Troublingly, an economy that can’t go on as we would like it to: a machine that spews out ever more stuff for ever more people. We really have reached limits for an industrial economy based on cheap, potent energy supplies. The energy, oil especially, isn’t cheap anymore. The fantasy that we can easily replace it with wind turbines, solar panels, and as-yet-unseen science projects is going to leave a lot of people not just disappointed but bereft, floundering, and probably dead, unless we make some pretty severe readjustments in daily life.
We’ve been papering this problem over by borrowing so much money from the future to cover costs today that eventually it will lose its meaning as money — that is, faith that it is worth anything. That’s what happens when money is just a representation of debt that can’t be paid back. This habit of heedless borrowing has enabled the country to pretend that it is functioning effectively. Lately, this game of pretend has sent the financial corps into a rapture of jubilation. The market speed bumps of February are behind us and the road ahead looks like the highway to Vegas at dawn on a summer’s day.
Tesla is the perfect metaphor for where the US economy is at: a company stuffed with debt plus government subsidies, unable to deliver the wished-for miracle product — affordable electric cars — whirling around the drain into bankruptcy. Tesla has been feeding one of the chief fantasies of the day: that we can banish climate problems caused by excessive CO2, while giving a new lease on life to the (actually) futureless suburban living arrangement that we foolishly invested so much of our earlier capital building. In other words, pounding sand down a rat hole.
Read more …

Yeah, we need more cars…
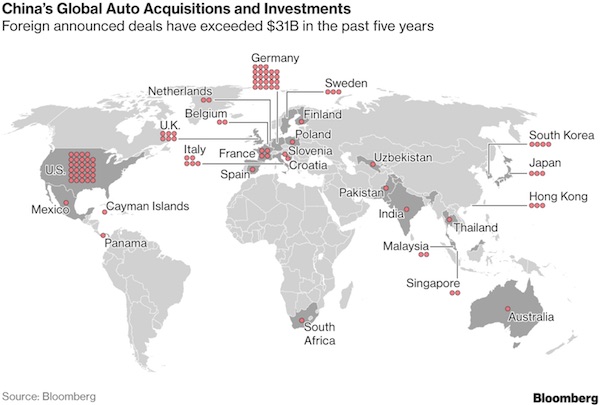
• The Chinese Car Invasion Is Coming (BBG)
On a bright spring day in Amsterdam, car buffs stepped inside a blacked-out warehouse to nibble on lamb skewers and sip rhubarb cocktails courtesy of Lynk & Co., which was showing off its new hybrid SUV. What seemed like just another launch of a new vehicle was actually something more: the coming-out party for China’s globally ambitious auto industry. For the first time, a Chinese-branded car will be made in Western Europe for sale there, with the ultimate goal of landing in U.S. showrooms.
That’s the master plan of billionaire Li Shufu, who has catapulted from founding Geely Group as a refrigerator maker in the 1980s to owning Volvo Cars, British sports carmaker Lotus, London Black Cabs and the largest stake in Daimler —the inventor of the automobile. Li is spearheading China’s aspirations to wedge itself among the big three of the global car industry—the U.S., Germany and Japan—so they become the Big Four. “I want the whole world to hear the cacophony generated by Geely and other made-in-China cars,” Li told Bloomberg News. “Geely’s dream is to become a globalized company. To do that, we must get out of the country.”
[..] Chinese companies have announced at least $31 billion in overseas deals during the past five years, buying stakes in carmakers and parts producers, according to data compiled by Bloomberg. The most prolific buyer is Li, who spent almost $13 billion on stakes in Daimler and truckmaker Volvo. Tencent Holdings Ltd., Asia’s biggest internet company, paid about $1.8 billion for 5% of Tesla. As software and electronics become just as critical to a car as the engine, China is ensuring it doesn’t lag behind in that market, either. Baidu, owner of the nation’s biggest search engine, announced a $1.5 billion Apollo Fund to invest in 100 autonomous-driving projects during the next three years.
“We have secured a chance to compete in the U.S. market of self-driving cars through those partnerships,” Li Zhengyu, a vice president overseeing Baidu’s intelligent-driving unit, told Bloomberg News. “Everyone has a good chance to win if it has good development plans.”
Read more …

The Troika demands that Greece kills its society even more. 4.2% of GDP disappears from the economy. Where it’s so badly needed.
• Greek Primary Surplus Comes At The Expense Of Growth (K.)
The 2017 budget has officially registered a record primary surplus of 4.2% of GDP, against a target for 1.75%, but this came at a particularly heavy price for the economy, which grew just 1.4% against a budget target for 2.7%. It is obvious that securing primary surpluses of more than twice the target, depriving the economy of precious resources, is directly associated with the stagnation of growth compared to original projections. It is no coincidence that consumption edged up just 0.1% last year, which analysts have attributed to taxpayers’ exhaustion due to overtaxation. The surplus was mainly a result of drastic cuts to the Public Investments Program (by about 800 million euros) and social benefits, due to the delay in the application of the Social Solidarity Income.
The government was quick to express its satisfaction upon the release of the fiscal results by the Hellenic Statistical Authority on Monday, although it was just two years ago that Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras accused the previous administration of setting excessive targets for the primary surpluses of 2016, 2017 and 2018 at 4.5% of GDP. Eventually he reached that target with his own government, although the creditors had lowered the bar, to 1.75% for 2017 and 3.5% this year. The Finance Ministry spoke yesterday of proof of “the credibility of the fiscal management,” adding that “those data show that not only is the target of 3.5% feasible for this and the coming years, but there will also be some fiscal space for targeted tax easing and social expenditure in the post-program period.”
That reference concerns the so-called “countermeasures” the government has planned in case it exceeds the 3.5% target in the 2019 and 2020 primary surpluses, but for now they are at the discretion of the IMF, which will decide next month whether they can be introduced. Obviously Athens hopes the 2017 figures will positively affect the Fund’s view. There was also a positive response from Brussels on Monday, with European Commissioner for Economic Affairs Pierre Moscovici and Commission spokesman Margaritis Schinas stating that the efforts and sacrifices of the Greek people are now paying dividend.
Read more …

The new head of the Greek Asylum Service flatly ignores the Council of State. Greek justice system overpowered by Brussels and Berlin.
• Tensions Grow On Greek Islands (K.)
Concerns have peaked over tensions on the Aegean islands following clashes between residents of Lesvos and migrants in Mytilene port which led to several injuries. Riot police were forced to intervene early Monday morning after dozens of local residents started protesting the presence of migrants in the main square of Mytilene. The migrants, who had been camping in the square since last Tuesday demanding to be allowed to leave the island, were put onto buses and taken back to overcrowded state facilities. According to local reports, the protesters threw flares, firecrackers and stones at the migrants, who formed a circle around women and children to protect them.
Some protesters chanted “Burn them alive,” according to reports which suggested that members of far-right groups were involved. Police detained 122 people – all but two of whom were Afghan migrants – while 28 people were transferred to the hospital for first-aid treatment, 22 of whom were migrants. Political parties issued statements blaming the attack on far-right groups. The mayor of Lesvos, Spyros Galinos, did not rule out the presence of extremists on the island but pointed to broader frustration among locals. “Society is reacting as a whole,” said Galinos, who had appealed to the government last week to reduce overcrowding on the islands.
[..] meanwhile, the new head of the Greek Asylum Service, Markos Karavias, signed an agreement effectively restricting migrants arriving on the Aegean islands from traveling on to the mainland. A Council of State ruling last week overturned previous asylum service restrictions on migrants leaving the islands. The government’s proposed changes to asylum laws – aimed at speeding up the slow pace at which applications are processed – are to be discussed in Parliament on Tuesday.
Read more …

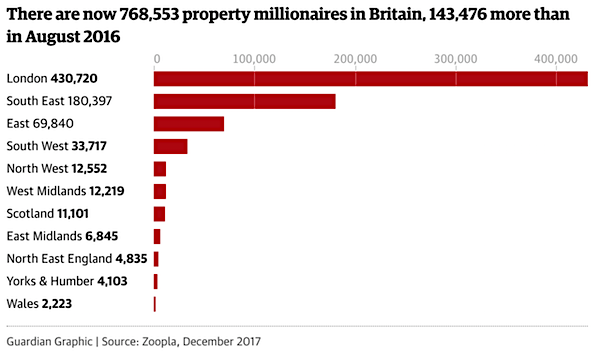
How poor Britain is becoming.
• The UK Has Turned The Right To Education Into A Charitable Cause (G.)
My nine-year-old son looks at me anxiously. “Mum, you definitely, definitely have my sponsor money plus an extra pound, which I need for the fundraising games. We have to bring it in today.” I search through my wallet for a quid each for him and his brother. I’ve got no cash on me. “We have to,” he repeats, his voice going wobbly. I stick an IOU in his piggy bank and the day is saved. Yet again. And yet again I feel infuriated and indignant at being put in this position. Then I feel even more cross that I now feel mean. Cake sale, plant sale, ticket for a pamper evening, music quiz, another cake sale, school disco (with associated plastic tat and penny sweets on sale), pay to see Santa, raffle for the chocolate hamper (that you’ve already sent in the goddamn chocolate for), dress up for World Book Day (that’s a quid), go pink for breast cancer research (that’s two quid) and why not run a sponsored mile for Sport Relief while you’re at it.
Then … ping! Oh joy, a text from school – another (another?!) cake sale. How much sugar is going down in that playground? The texts keep flooding in. Ransack your wardrobe for Bag 2 School; send in dosh so your child can buy you a Mother’s Day present; scrabble through your (now denuded) wardrobe for next week’s clothes swap and pretty please, the PTA would appreciate donations of booze for this year’s summer fete. If enough of you don’t stump up by Friday, you’ll be harangued daily until you do. Welcome to summer term, peak time for school fundraising – and what feels like a constant assault. Let’s put aside my irritation at being “chugged” via leaflets in book-bags and my mobile phone, in principle it’s a good thing for kids to think about the needs of people other than themselves, so I’ll swallow official charity fundraisers on that basis, even if those charities might not be my personal choice.
What is outrageous, though, is the assumption in some schools that parents can easily afford to donate on a virtually weekly basis, and the idea that we should expect to be paying on top of our taxes for our children’s state education. Schools, suffering the terrible results of the government’s austerity policies, have cut to the chase and are now pumping parents for regular direct debits to cover essentials. But is asking parents to pay doing pupils’ education any good?
Read more …

No surprise.
• UK Food Bank Use Reaches Highest Rate On Record (Ind.)
Food bank use has soared at a higher rate than ever in the past year as welfare benefits fail to cover basic living costs, the UK’s national food bank provider has warned. Figures from the Trussel Trust show that in the year to March 2018, 1,332,952 three-day emergency food supplies were delivered to people in crisis across the UK – a 13% increase on last year. This marks a considerably higher increase than the previous financial year, when it rose by 6%. Low income is the biggest single – and fastest growing – reason for referral to food banks, accounting for 28% of referrals compared to 26% in the previous year. Analysis of trends over time demonstrates it has significantly increased since April 2016.
Being in debt also accounted for an increasing percentage of referrals – at 9% of referrals up from 8% in the past year. The cost of housing and utility bills are increasingly driving food bank referrals for this reason, with the proportion of referrals due to housing debt and utility bill debt increasing significantly since April 2016. The other main primary referral reasons in the past year were benefit delays (24%) and benefit changes (18%). “Reduction in benefit value” have the fastest growth rate of all referrals made due to a benefit change, while those due to “moving to a different benefit” have also grown significantly.
Read more …

It’s dangerous when people trial basic income schemes who don’t understand them. Others will say: it failed in Finland! No it didn’t. It has to be universal, and this is not.
• Finland To End Basic Income Trial After Two Years (G.)
Europe’s first national government-backed experiment in giving citizens free cash will end next year after Finland decided not to extend its widely publicised basic income trial and to explore alternative welfare schemes instead. Since January 2017, a random sample of 2,000 unemployed people aged 25 to 58 have been paid a monthly €560 (£475) , with no requirement to seek or accept employment. Any recipients who took a job continued to receive the same amount. The government has turned down a request for extra funding from Kela, the Finnish social security agency, to expand the two-year pilot to a group of employees this year, and said payments to current participants will end next January.
It has also introduced legislation making some benefits for unemployed people contingent on taking training or working at least 18 hours in three months. “The government is making changes taking the system away from basic income,” Kela’s Miska Simanainen told the Swedish newspaper Svenska Dagbladet. The scheme – aimed primarily at seeing whether a guaranteed income might incentivise people to take up paid work by smoothing out gaps in the welfare system – is strictly speaking not a universal basic income (UBI) trial, because the payments are made to a restricted group and are not enough to live on.
But it was hoped it would shed light on policy issues such as whether an unconditional payment might reduce anxiety among recipients and allow the government to simplify a complex social security system that is struggling to cope with a fast-moving and insecure labour market. Olli Kangas, an expert involved in the trial, told the Finnish public broadcaster YLE: “Two years is too short a period to be able to draw extensive conclusions from such a big experiment. We should have had extra time and more money to achieve reliable results.”
Read more …